Target mRNA abundance dilutes microRNA and siRNA activity
- PMID: 20404830
- PMCID: PMC2872614
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2010.24
Target mRNA abundance dilutes microRNA and siRNA activity
Abstract
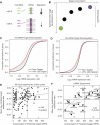
Post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs and siRNAs depends not only on characteristics of individual binding sites in target mRNA molecules, but also on system-level properties such as overall molecular concentrations. We hypothesize that an intracellular pool of microRNAs/siRNAs faced with a larger number of available predicted target transcripts will downregulate each individual target gene to a lesser extent. To test this hypothesis, we analyzed mRNA expression change from 178 microRNA and siRNA transfection experiments in two cell lines. We find that downregulation of particular genes mediated by microRNAs and siRNAs indeed varies with the total concentration of available target transcripts. We conclude that to interpret and design experiments involving gene regulation by small RNAs, global properties, such as target mRNA abundance, need to be considered in addition to local determinants. We propose that analysis of microRNA/siRNA targeting would benefit from a more quantitative definition, rather than simple categorization of genes as 'target' or 'not a target.' Our results are important for understanding microRNA regulation and may also have implications for siRNA design and small RNA therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Farh K, Grimson A, Jan C, Lewis B, Johnston W, Lim L, Burge C, Bartel D (2005) The widespread impact of mammalian microRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science 310: 1817–1821 - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya S, Sonenberg N (2008) Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 9: 102–114 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

