Circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor and indices of metabolic and cardiovascular health: data from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging
- PMID: 20404913
- PMCID: PMC2852401
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010099
Circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor and indices of metabolic and cardiovascular health: data from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging
Abstract
Background: Besides its well-established role in nerve cell survival and adaptive plasticity, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is also involved in energy homeostasis and cardiovascular regulation. Although BDNF is present in the systemic circulation, it is unknown whether plasma BDNF correlates with circulating markers of dysregulated metabolism and an adverse cardiovascular profile.
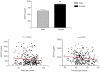
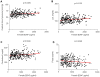
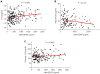
Methodology/principal findings: To determine whether circulating BDNF correlates with indices of metabolic and cardiovascular health, we measured plasma BDNF levels in 496 middle-age and elderly subjects (mean age approximately 70), in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Linear regression analysis revealed that plasma BDNF is associated with risk factors for cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome, regardless of age. In females, BDNF was positively correlated with BMI, fat mass, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, and LDL-cholesterol, and inversely correlated with folate. In males, BDNF was positively correlated with diastolic blood pressure, triglycerides, free thiiodo-thyronine (FT3), and bioavailable testosterone, and inversely correlated with sex-hormone binding globulin, and adiponectin.
Conclusion/significance: Plasma BDNF significantly correlates with multiple risk factors for metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular dysfunction. Whether BDNF contributes to the pathogenesis of these disorders or functions in adaptive responses to cellular stress (as occurs in the brain) remains to be determined.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
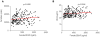

Similar articles
-
The relationship between serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and cardiometabolic indices in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2014 Aug;157(1-3):244-8. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.05.024. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Schizophr Res. 2014. PMID: 24934904
-
Circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor concentrations and the risk of cardiovascular disease in the community.J Am Heart Assoc. 2015 Mar 11;4(3):e001544. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001544. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015. PMID: 25762803 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor is related to cardiovascular risk factors in active and inactive elderly men.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016 Jun 20;49(7):e5253. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20165253. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016. PMID: 27332774 Free PMC article.
-
Cortisol:brain-derived neurotrophic factor ratio associated with silent ischaemia in a black male cohort: the SA BPA study.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2016 Nov/Dec;27(6):387-391. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2016-065. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2016. PMID: 27966001 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrative Review of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Serious Cardiovascular Conditions.Nurs Res. 2020 Sep/Oct;69(5):376-390. doi: 10.1097/NNR.0000000000000454. Nurs Res. 2020. PMID: 32555009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of recombinant erythropoietin on plasma brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in patients with affective disorders: a randomised controlled study.PLoS One. 2015 May 26;10(5):e0127629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127629. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26011424 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Vildagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, attenuated endothelial dysfunction through miRNAs in diabetic rats.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Jul 12;17(5):1378-1387. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.86609. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 34522267 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin B12 and Homocysteine Associations with Gait Speed in Older Adults: The Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging.J Nutr Health Aging. 2017;21(10):1321-1328. doi: 10.1007/s12603-017-0893-4. J Nutr Health Aging. 2017. PMID: 29188896 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Has Diagnostic and Prognostic Value in Traumatic Brain Injury.J Neurotrauma. 2016 Jan 15;33(2):215-25. doi: 10.1089/neu.2015.3949. Epub 2015 Sep 18. J Neurotrauma. 2016. PMID: 26159676 Free PMC article.
-
Measurements in the Blood of BDNF for RA Patients and in Response to Anti-TNF Treatment Help Us to Clarify the Magnitude of Centrally Related Pain and to Explain the Relief of This Pain upon Treatment.Int J Inflam. 2011;2011:650685. doi: 10.4061/2011/650685. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Int J Inflam. 2011. PMID: 21755028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barde YA. Neurotrophins: A family of proteins supporting the survival of neurons. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1994;390:45–56. - PubMed
-
- Mattson MP, Maudsley S, Martin B. A neural signaling triumvirate that influences ageing and age-related disease: Insulin/IGF-1, BDNF and serotonin. Ageing Res Rev. 2004;3:445–464. - PubMed
-
- Nakahashi T, Fujimara H, Altar CA, Li J, Kambayashi J, et al. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Letters. 2000;470:113–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

