Modular insulators: genome wide search for composite CTCF/thyroid hormone receptor binding sites
- PMID: 20404925
- PMCID: PMC2852416
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010119
Modular insulators: genome wide search for composite CTCF/thyroid hormone receptor binding sites
Abstract
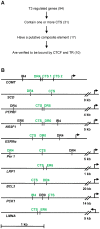
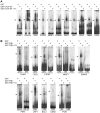
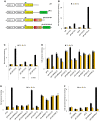
The conserved 11 zinc-finger protein CTCF is involved in several transcriptional mechanisms, including insulation and enhancer blocking. We had previously identified two composite elements consisting of a CTCF and a TR binding site at the chicken lysozyme and the human c-myc genes. Using these it has been demonstrated that thyroid hormone mediates the relief of enhancer blocking even though CTCF remains bound to its binding site. Here we wished to determine whether CTCF and TR combined sites are representative of a general feature of the genome, and whether such sites are functional in regulating enhancer blocking. Genome wide analysis revealed that about 18% of the CTCF regions harbored at least one of the four different palindromic or repeated sequence arrangements typical for the binding of TR homodimers or TR/RXR heterodimers. Functional analysis of 10 different composite elements of thyroid hormone responsive genes was performed using episomal constructs. The episomal system allowed recapitulating CTCF mediated enhancer blocking function to be dependent on poly (ADP)-ribose modification and to mediate histone deacetylation. Furthermore, thyroid hormone sensitive enhancer blocking could be shown for one of these new composite elements. Remarkably, not only did the regulation of enhancer blocking require functional TR binding, but also the basal enhancer blocking activity of CTCF was dependent on the binding of the unliganded TR. Thus, a number of composite CTCF/TR binding sites may represent a subset of other modular CTCF composite sites, such as groups of multiple CTCF sites or of CTCF/Oct4, CTCF/Kaiso or CTCF/Yy1 combinations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
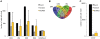

Similar articles
-
Thyroid hormone-regulated enhancer blocking: cooperation of CTCF and thyroid hormone receptor.EMBO J. 2003 Apr 1;22(7):1579-87. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg147. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12660164 Free PMC article.
-
The thyroid hormone receptor and the insulator protein CTCF: two different factors with overlapping functions.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002 Dec;83(1-5):49-57. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(02)00256-x. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12650701 Review.
-
CTCF is conserved from Drosophila to humans and confers enhancer blocking of the Fab-8 insulator.EMBO Rep. 2005 Feb;6(2):165-70. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400334. EMBO Rep. 2005. PMID: 15678159 Free PMC article.
-
Negative transcriptional regulation mediated by thyroid hormone response element 144 requires binding of the multivalent factor CTCF to a novel target DNA sequence.J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 17;274(38):27092-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.38.27092. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10480923
-
Modulation of thyroid hormone receptor silencing function by co-repressors and a synergizing transcription factor.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):386-9. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961925 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide binding patterns of thyroid hormone receptor beta.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 18;9(2):e81186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081186. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24558356 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of gene expression in the genomic context.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2014 Jan 29;9:e201401001. doi: 10.5936/csbj.201401001. eCollection 2014. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2014. PMID: 24688749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C2H2-Type Zinc Finger Proteins: Evolutionarily Old and New Partners of the Nuclear Hormone Receptors.Nucl Recept Signal. 2018 Oct 24;15:1550762918801071. doi: 10.1177/1550762918801071. eCollection 2018. Nucl Recept Signal. 2018. PMID: 30718982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D receptor controls expression of the anti-aging klotho gene in mouse and human renal cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Oct 28;414(3):557-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.09.117. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21982773 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 is a direct coactivator of thyroid hormone receptor β1 with gene-specific actions.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 26;8(7):e70097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070097. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23922917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vostrov AA, Quitschke WW. The zinc finger protein CTCF binds to the APBbeta domain of the amyloid beta-protein precursor promoter. Evidence for a role in transcriptional activation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:33353–33359. - PubMed
-
- Baniahmad A, Steiner C, Kohne AC, Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990;61:505–514. - PubMed
-
- Lobanenkov VV, Nicolas RH, Adler VV, Paterson H, Klenova EM, et al. A novel sequence-specific DNA binding protein which interacts with three regularly spaced direct repeats of the CCCTC-motif in the 5′- flanking sequence of the chicken c-myc gene. Oncogene. 1990;5:1743–1753. - PubMed
-
- Bell AC, West AG, Felsenfeld G. The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell. 1999;98:387–396. - PubMed
-
- Filippova GN, Thienes CP, Penn BH, Cho DH, Hu YJ, et al. CTCF-binding sites flank CTG/CAG repeats and form a methylation- sensitive insulator at the DM1 locus. Nat Genet. 2001;28:335–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

