Small molecules showing significant protection of mice against botulinum neurotoxin serotype A
- PMID: 20405003
- PMCID: PMC2854131
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010129
Small molecules showing significant protection of mice against botulinum neurotoxin serotype A
Abstract
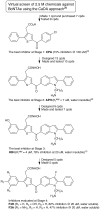
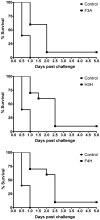
Botulinum neurotoxin serotype A (BoNTA) causes a life-threatening neuroparalytic disease known as botulism that could afflict large, unprotected populations if the toxin were employed in an act of bioterrorism. Current post-exposure therapy is limited to symptomatic treatment or passive immunization that is effective for treating infant botulism at a cost of US $45,300 per treatment regimen. Antibodies can neutralize the extracellular but not the intracellular BoNTA. Moreover, antibody production, storage, and administration in a mass casualty scenario pose logistical challenges. Alternatively, small-molecule inhibitors of BoNTA endopeptidase (BoNTAe) are sought to antagonize the extracellular or intracellular toxin. While several such molecules reportedly demonstrated efficacy in protecting cells against BoNTA, there is scant information to show that small molecules can significantly protect mammals against BoNTA. Herein we report the development of effective small-molecules BoNTAe inhibitors with promising in vivo pharmacokinetics. One such molecule has an in vivo half-life of 6.5 hours and is devoid of obvious sign of toxicity. Pre-treatment with this molecule at 2 mg/kg protected 100% and 70% of treated mice against BoNTA at 5 times of its median-lethal dose during the periods of 2 and 4 half-lives of the inhibitor, respectively. In contrast, 40% and 0% of untreated mice survived during the respective periods. Similar levels of protection were also observed with two other small molecules. These results demonstrate that small molecules can significantly protect mice against BoNTA and support the pursuit of small-molecule antagonists as a cost-effective alternative or as an adjunct to passive immunity for treating botulism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potent new small-molecule inhibitor of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A endopeptidase developed by synthesis-based computer-aided molecular design.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 10;4(11):e7730. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007730. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19901994 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to Counteract Botulinum Neurotoxin A: Nature's Deadliest Biomolecule.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Aug 20;52(8):2322-2331. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00261. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31322847 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule metalloprotease inhibitor with in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo efficacy against botulinum neurotoxin serotype A.Toxicon. 2017 Oct;137:36-47. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2017.06.016. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Toxicon. 2017. PMID: 28698055 Free PMC article.
-
The science and manufacturing behind botulinum neurotoxin type A-ABO in clinical use.Aesthet Surg J. 2009 Nov;29(6 Suppl):S34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.asj.2009.09.014. Aesthet Surg J. 2009. PMID: 19945003 Review.
-
Strategies to design inhibitors of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2007 Mar;7(1):47-57. doi: 10.2174/187152607780090667. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17346211 Review.
Cited by
-
Substrate-based inhibitors exhibiting excellent protective and therapeutic effects against Botulinum Neurotoxin A intoxication.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 20;5:16981. doi: 10.1038/srep16981. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26584873 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the Pharmacokinetic Properties of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A Protease Inhibitors Through Rational Design.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011 Jun 15;2(6):288-293. doi: 10.1021/cn200021q. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21743830 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into exosite binding and discovery of novel exosite inhibitors of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A through in silico screening.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014 Jul;28(7):765-78. doi: 10.1007/s10822-014-9758-7. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2014. PMID: 24958623 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance and Recent Alternatives to Antibiotics for the Control of Bacterial Pathogens with an Emphasis on Foodborne Pathogens.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 30;12(2):274. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020274. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecule inhibitors as countermeasures for botulinum neurotoxin intoxication.Molecules. 2010 Dec 30;16(1):202-20. doi: 10.3390/molecules16010202. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 21193845 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shapiro RL, Hatheway C, Swerdlow DL. Botulism in the United States - a clinical and epidemiologic review. Ann Intern Med. 1998;129:221–228. - PubMed
-
- Kessler KR, Benecke R. Botulinum toxin—from poison to remedy. Neurotoxicology. 1997;18:761–770. - PubMed
-
- Springen K, Raymond J, Skipp C, Scelfo J, SS. The Botox boom. Newsweek. 2002. pp. 50–58.
-
- Crowner BE, Brunstrom JE, Racette BA. Iatrogenic botulism due to therapeutic botulinum toxin A injection in a pediatric patient. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2007;30:310–313. - PubMed
-
- Kuehn BM. FDA requires black box warnings on labeling for botulinum toxin products. JAMA. 2009;301:2316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

