A monoclonal antibody toolkit for C. elegans
- PMID: 20405020
- PMCID: PMC2854156
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010161
A monoclonal antibody toolkit for C. elegans
Abstract
Background: Antibodies are critical tools in many avenues of biological research. Though antibodies can be produced in the research laboratory setting, most research labs working with vertebrates avail themselves of the wide array of commercially available reagents. By contrast, few such reagents are available for work with model organisms.
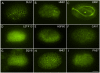
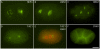
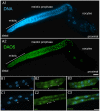
Methodology/principal findings: We report the production of monoclonal antibodies directed against a wide range of proteins that label specific subcellular and cellular components, and macromolecular complexes. Antibodies were made to synaptobrevin (SNB-1), a component of synaptic vesicles; to Rim (UNC-10), a protein localized to synaptic active zones; to transforming acidic coiled-coil protein (TAC-1), a component of centrosomes; to CENP-C (HCP-4), which in worms labels the entire length of their holocentric chromosomes; to ORC2 (ORC-2), a subunit of the DNA origin replication complex; to the nucleolar phosphoprotein NOPP140 (DAO-5); to the nuclear envelope protein lamin (LMN-1); to EHD1 (RME-1) a marker for recycling endosomes; to caveolin (CAV-1), a marker for caveolae; to the cytochrome P450 (CYP-33E1), a resident of the endoplasmic reticulum; to beta-1,3-glucuronyltransferase (SQV-8) that labels the Golgi; to a chaperonin (HSP-60) targeted to mitochondria; to LAMP (LMP-1), a resident protein of lysosomes; to the alpha subunit of the 20S subcomplex (PAS-7) of the 26S proteasome; to dynamin (DYN-1) and to the alpha-subunit of the adaptor complex 2 (APA-2) as markers for sites of clathrin-mediated endocytosis; to the MAGUK, protein disks large (DLG-1) and cadherin (HMR-1), both of which label adherens junctions; to a cytoskeletal linker of the ezrin-radixin-moesin family (ERM-1), which localized to apical membranes; to an ERBIN family protein (LET-413) which localizes to the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells and to an adhesion molecule (SAX-7) which localizes to the plasma membrane at cell-cell contacts. In addition to working in whole mount immunocytochemistry, most of these antibodies work on western blots and thus should be of use for biochemical fractionation studies.
Conclusions/significance: We have produced a set of monoclonal antibodies to subcellular components of the nematode C. elegans for the research community. These reagents are being made available through the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular and functional analysis of apical junction formation in the gut epithelium of Caenorhabditis elegans.Dev Biol. 2004 Feb 1;266(1):17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.10.019. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 14729475
-
The C. elegans ezrin-radixin-moesin protein ERM-1 is necessary for apical junction remodelling and tubulogenesis in the intestine.Dev Biol. 2004 Aug 1;272(1):262-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.05.012. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15242805
-
UNC-11, a Caenorhabditis elegans AP180 homologue, regulates the size and protein composition of synaptic vesicles.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Jul;10(7):2343-60. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.7.2343. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10397769 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolae and caveolin isoforms in rat peritoneal macrophages.Micron. 2002;33(1):75-93. doi: 10.1016/s0968-4328(00)00100-1. Micron. 2002. PMID: 11473817 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms in clathrin-mediated membrane budding revealed through subcellular proteomics.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Nov;32(Pt 5):769-73. doi: 10.1042/BST0320769. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15494011 Review.
Cited by
-
Detecting gene expression in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2025 Jan 8;229(1):1-108. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae167. Genetics. 2025. PMID: 39693264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An instructive role for C. elegans E-cadherin in translating cell contact cues into cortical polarity.Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Jun;17(6):726-35. doi: 10.1038/ncb3168. Epub 2015 May 4. Nat Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25938815 Free PMC article.
-
Direct experimental manipulation of intestinal cells in Ascaris suum, with minor influences on the global transcriptome.Int J Parasitol. 2017 Apr;47(5):271-279. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.12.005. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Int J Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28223178 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans BLOC-1 functions in trafficking to lysosome-related gut granules.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43043. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043043. Epub 2012 Aug 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22916203 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity-linked genes are stimulated by a membrane stress pathway linked to Golgi function and the ARF-1 GTPase.Sci Adv. 2023 Dec 8;9(49):eadi5545. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi5545. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38055815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duerr JS, Han HP, Fields SD, Rand JB. Identification of major classes of cholinergic neurons in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Comp Neurol. 2008;506:398–408. - PubMed
-
- Nance J, Munro EM, Priess JR. C. elegans PAR-3 and PAR-6 are required for apicobasal asymmetries associated with cell adhesion and gastrulation. Development. 2003;130:5339–5350. - PubMed
-
- Inoue T, Takashima M, Murakami S, Watanabe T. Partial characterization of the antigen recognized by a monoclonal antibody to Ascaris suum ovary extracts. Vet Parasitol. 2007;146:281–287. - PubMed
-
- Ladurner P, Pfister D, Seifarth C, Scharer L, Mahlknecht M, et al. Production and characterisation of cell- and tissue-specific monoclonal antibodies for the flatworm Macrostomum sp. Histochem Cell Biol. 2005;123:89–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

