Sequencing and genetic variation of multidrug resistance plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 20405037
- PMCID: PMC2853573
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010141
Sequencing and genetic variation of multidrug resistance plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
Background: The development of multidrug resistance is a major problem in the treatment of pathogenic microorganisms by distinct antimicrobial agents. Characterizing the genetic variation among plasmids from different bacterial species or strains is a key step towards understanding the mechanism of virulence and their evolution.
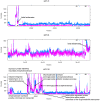
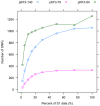
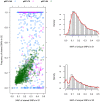
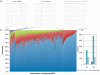
Results: We applied a deep sequencing approach to 206 clinical strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae collected from 2002 to 2008 to understand the genetic variation of multidrug resistance plasmids, and to reveal the dynamic change of drug resistance over time. First, we sequenced three plasmids (70 Kb, 94 Kb, and 147 Kb) from a clonal strain of K. pneumoniae using Sanger sequencing. Using the Illumina sequencing technology, we obtained more than 17 million of short reads from two pooled plasmid samples. We mapped these short reads to the three reference plasmid sequences, and identified a large number of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in these pooled plasmids. Many of these SNPs are present in drug-resistance genes. We also found that a significant fraction of short reads could not be mapped to the reference sequences, indicating a high degree of genetic variation among the collection of K. pneumoniae isolates. Moreover, we identified that plasmid conjugative transfer genes and antibiotic resistance genes are more likely to suffer from positive selection, as indicated by the elevated rates of nonsynonymous substitution.
Conclusion: These data represent the first large-scale study of genetic variation in multidrug resistance plasmids and provide insight into the mechanisms of plasmid diversification and the genetic basis of antibiotic resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Shen P, Jiang Y, Zhou Z, Zhang J, Yu Y, et al. Complete nucleotide sequence of pKP96, a 67 850 bp multiresistance plasmid encoding qnrA1, aac(6′)-Ib-cr and blaCTX-M-24 from Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;62:1252–1256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

