A vertebrate-specific Chp-PAK-PIX pathway maintains E-cadherin at adherens junctions during zebrafish epiboly
- PMID: 20405038
- PMCID: PMC2853574
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010125
A vertebrate-specific Chp-PAK-PIX pathway maintains E-cadherin at adherens junctions during zebrafish epiboly
Abstract
Background: In early vertebrate development, embryonic tissues modulate cell adhesiveness and acto-myosin contractility to correctly orchestrate the complex processes of gastrulation. E-cadherin (E-cadh) is the earliest expressed cadherin and is needed in the mesendodermal progenitors for efficient migration. Regulatory mechanisms involving directed E-cadh trafficking have been invoked downstream of Wnt11/5 signaling. This non-canonical Wnt pathway regulates RhoA-ROK/DAAM1 to control the acto-myosin network. However, in this context nothing is known of the intracellular signals that participate in the correct localization of E-cadh, other than a need for Rab5c signaling.
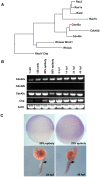
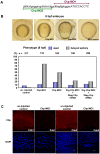
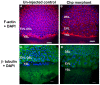
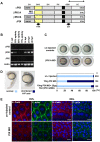
Methodology/principal findings: By studying loss of Chp induced by morpholino-oligonucleotide injection in zebrafish, we find that the vertebrate atypical Rho-GTPase Chp is essential for the proper disposition of cells in the early embryo. The underlying defect is not leading edge F-actin assembly (prominent in the cells of the envelope layer), but rather the failure to localize E-cadh and beta-catenin at the adherens junctions. Loss of Chp results in delayed epiboly that can be rescued by mRNA co-injection, and phenocopies zebrafish E-cadh mutants. This new signaling pathway involves activation of an effector kinase PAK, and involvement of the adaptor PAK-interacting exchange factor PIX. Loss of signaling by any of the three components results in similar underlying defects, which is most prominent in the epithelial-like envelope layer.
Conclusions/significance: Our current study uncovers a developmental pathway involving Chp/PAK/PIX signaling, which helps co-ordinate E-cadh disposition to promote proper cell adhesiveness, and coordinate movements of the three major cell layers in epiboly. Our data shows that without Chp signaling, E-cadh shifts to intracellular vesicles rather than the adhesive contacts needed for directed cell movement. These events may mirror the requirement for PAK2 signaling essential for the proper formation of the blood-brain barrier.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
A βPIX-PAK2 complex confers protection against Scrib-dependent and cadherin-mediated apoptosis.Curr Biol. 2012 Oct 9;22(19):1747-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.07.011. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22863318 Free PMC article.
-
Galpha12/13 regulate epiboly by inhibiting E-cadherin activity and modulating the actin cytoskeleton.J Cell Biol. 2009 Mar 23;184(6):909-21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200805148. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19307601 Free PMC article.
-
The atypical Rho GTPase, RhoU, regulates cell-adhesion molecules during cardiac morphogenesis.Dev Biol. 2014 May 15;389(2):182-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.02.014. Epub 2014 Mar 7. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24607366 Free PMC article.
-
Abl tyrosine kinases modulate cadherin-dependent adhesion upstream and downstream of Rho family GTPases.Cell Cycle. 2008 Feb 15;7(4):444-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.4.5452. Epub 2007 Dec 12. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18235247 Review.
-
Epithelial junctions and Rho family GTPases: the zonular signalosome.Small GTPases. 2014;5(4):1-15. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973760. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25483301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of a single-copy DAAM1 gene in congenital heart defect: a case report.BMC Med Genet. 2012 Aug 2;13:63. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-13-63. BMC Med Genet. 2012. PMID: 22857009 Free PMC article.
-
A βPIX-PAK2 complex confers protection against Scrib-dependent and cadherin-mediated apoptosis.Curr Biol. 2012 Oct 9;22(19):1747-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.07.011. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22863318 Free PMC article.
-
Rho family GTPase Chp/RhoV induces PC12 apoptotic cell death via JNK activation.Small GTPases. 2011 Jan;2(1):17-26. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.2.1.15229. Small GTPases. 2011. PMID: 21686277 Free PMC article.
-
The ceramide synthase 2b gene mediates genomic sensing and regulation of sphingosine levels during zebrafish embryogenesis.Elife. 2017 Sep 28;6:e21992. doi: 10.7554/eLife.21992. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28956531 Free PMC article.
-
RHOV is a Detachment-Responsive Rho GTPase Necessary for Ovarian Cancer Peritoneal Metastasis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 13:2025.08.12.669944. doi: 10.1101/2025.08.12.669944. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40832333 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Babb SG, Marrs JA. E-cadherin regulates cell movements and tissue formation in early zebrafish embryos. Dev Dyn. 2004;230:263–277. - PubMed
-
- Montero JA, Carvalho L, Wilsch-Brauninger M, Kilian B, Mustafa C, et al. Shield formation at the onset of zebrafish gastrulation. Development. 2005;132:1187–1198. - PubMed
-
- Ulrich F, Krieg M, Schotz EM, Link V, Castanon I, et al. Wnt11 functions in gastrulation by controlling cell cohesion through Rab5c and E-cadherin. Dev Cell. 2005;9:555–564. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu T, Yabe T, Muraoka O, Yonemura S, Aramaki S, et al. E-cadherin is required for gastrulation cell movements in zebrafish. Mech Dev. 2005;122:747–763. - PubMed
-
- Kane DA, McFarland KN, Warga RM. Mutations in half baked/E-cadherin block cell behaviors that are necessary for teleost epiboly. Development. 2005;132:1105–1116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

