Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a promising biomarker for human acute kidney injury
- PMID: 20406069
- PMCID: PMC2893148
- DOI: 10.2217/bmm.10.12
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a promising biomarker for human acute kidney injury
Abstract
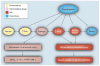
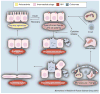
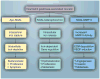
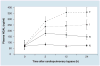
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and serious condition, the diagnosis of which depends on serum creatinine measurements. Unfortunately, creatinine is a delayed and unreliable indicator of AKI. The lack of early biomarkers has crippled our ability to translate promising experimental therapies to human AKI. Fortunately, understanding the early stress response of the kidney to acute injuries has revealed a number of potential biomarkers. The discovery, translation and validation of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, arguably the most promising novel AKI biomarker, are reviewed in this article. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is emerging as an excellent standalone troponin-like biomarker in the plasma and urine for the prediction of AKI, monitoring clinical trials in AKI and for the prognosis of AKI in several common clinical scenarios.
Figures

References
Bibliography
-
- Murray PT, Devarajan P, Level AS, et al. A framework and key research questions in AKI diagnosis and staging in different environments. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:864–868. Novel approach to clinical staging of acute kidney injury (AKI) - PubMed
-
- Devarajan P. Update on mechanisms of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1503–1520. Comprehensive review of the pathophysiologic mechanisms that underlie AKI. - PubMed
-
- Nickolas TL, Barasch J, Devarajan P. Biomarkers in acute and chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2008;17:127–132. - PubMed
-
- Devarajan P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin – an emerging troponin for kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23(12):3737–3743. Comprehensive review of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker of AKI, in comparison with other novel biomarkers. - PMC - PubMed
Website
-
- US FDA. Challenges and Opportunities Report. Mar, 2004. www.fda.gov/ScienceResearch/SpecialTopics/CriticalPathInitiative/Critica....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
