Translational pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling; application to cardiovascular safety data for PF-00821385, a novel HIV agent
- PMID: 20406218
- PMCID: PMC2848407
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03594.x
Translational pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling; application to cardiovascular safety data for PF-00821385, a novel HIV agent
Abstract
Aim: To assess the translation of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) relationships for heart rate effects of PF-00821385 in dog and man.
Methods: Cardiovascular telemetric parameters and concentration data were available for animals receiving active doses (0.5-120 mg kg(-1), n= 4) or vehicle. PF-00821385 was administered to 24 volunteers and pharmacokinetic and vital signs data were collected. PK-PD models were fitted using nonlinear mixed effects.
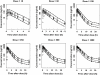
Results: Compartmental models with linear absorption and clearance were used to describe pharmacokinetic disposition in animal and man. Diurnal variation in heart and pulse rate was best described with a single cosine function in both dog and man. Canine and human heart rate change were described by a linear model with free drug slope 1.76 bpm microM(-1)[95% confidence interval (CI) 1.17, 2.35] in the dog and 0.76 bpm microM(-1) (95% CI 0.54, 1.14) in man.
Conclusions: The preclinical translational of concentration-response has been described and the potential for further interspecies extrapolation and optimization of clinical trial design is addressed.
Figures




References
-
- Poignard P, Saphire EO, Parren PW, Burton DR. gp120: biological aspects of structural features. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:253–74. - PubMed
-
- Danhof M, de Lange EC, Della Pasqua OE, Ploeger BA, Voskuyl RA. Mechanism-based pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic (PK–PD) modeling in translational drug research. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2008;29:186–91. - PubMed
-
- Beal SL, Boeckmann AJ. San Francisco, CA: University of California; NONMEM Users Guides. 1989–1998.
-
- Jonsson EN, Karlsson MO. Xpose – an S-PLUS based population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model building aid for NONMEM. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 1999;58:51–64. - PubMed
-
- Lindbom L, Pihlgren P, Jonsson EN. PsN-Toolkit – a collection of computer intensive statistical methods for non-linear mixed effect modeling using NONMEM. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2005;79:241–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

