Population pharmacokinetics and Bayesian estimator of mycophenolic acid in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome
- PMID: 20406220
- PMCID: PMC2848409
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03615.x
Population pharmacokinetics and Bayesian estimator of mycophenolic acid in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome
Abstract
Aims: To develop a population pharmacokinetic model for mycophenolic acid (MPA) in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) treated with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), identify covariates that explain variability and determine the Bayesian estimator of the area under the concentration-time curve over 12 h (AUC(0-12)).
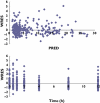
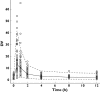
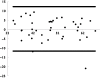
Methods: The pharmacokinetic model of MMF was described from 23 patients aged 7.4 +/- 3.9 years (range 2.9-14.9) using nonlinear mixed-effects modelling (NONMEM) software. A two-compartment model with lag-time and first-order absorption and elimination was developed. The final model was validated using visual predictive check. Bayesian estimator was validated using circular permutation method.
Results: The population pharmacokinetic parameters were apparent oral clearance 9.7 l h(-1), apparent central volume of distribution 22.3 l, apparent peripheral volume of distribution 250 l, inter-compartment clearance 18.8 l h(-1), absorption rate constant 5.16 h(-1), lag time 0.215 h. The covariate analysis identified body weight and serum albumin as individual factors influencing the apparent oral clearance. Accurate Bayesian estimation of AUC(0-12) was obtained using the combination of three MPA concentrations measured just before (T(0)), 1 and 4 h (T(1) and T(4)) after drug intake with a small error of 0.298 microg h(-1) ml(-1) between estimated and reference AUC(0-12).
Conclusions: The population pharmacokinetic model of MPA was developed in children with INS. A three-point (T(0), T(1) and T(4)h) Bayesian estimator of AUC(0-12) was developed and might be used to investigate the relation between MPA pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics in children with INS and determine if there is any indication to monitor MPA exposure in order to improve patient outcome based on individual AUC-controlled MMF dosing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Limited sampling models and Bayesian estimation for mycophenolic acid area under the curve prediction in stable renal transplant patients co-medicated with ciclosporin or sirolimus.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009;48(11):745-58. doi: 10.2165/11318060-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009. PMID: 19817503
-
Development of a Bayesian estimator for the therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolate mofetil in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome.Pharmacol Res. 2011 May;63(5):423-31. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2011.01.009. Epub 2011 Jan 25. Pharmacol Res. 2011. PMID: 21272643
-
Bayesian estimation of mycophenolate mofetil in lung transplantation, using a population pharmacokinetic model developed in kidney and lung transplant recipients.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012 Jan 1;51(1):29-39. doi: 10.2165/11594050-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012. PMID: 22054177 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mycophenolate in patients with autoimmune disease.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013 May;52(5):303-31. doi: 10.1007/s40262-013-0039-8. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013. PMID: 23475567 Review.
-
Mycophenolate, clinical pharmacokinetics, formulations, and methods for assessing drug exposure.Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2011 Apr;25(2):47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2011. PMID: 21190834
Cited by
-
Developmental changes of MPA exposure in children.Pediatr Nephrol. 2016 Jun;31(6):975-82. doi: 10.1007/s00467-015-3303-3. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Pediatr Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26743220
-
Significant Effects of Renal Function on Mycophenolic Acid Total Clearance in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients with Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2023 Sep;62(9):1289-1303. doi: 10.1007/s40262-023-01280-0. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2023. PMID: 37493886
-
Maximum a posteriori Bayesian estimation of mycophenolic Acid area under the concentration-time curve: is this clinically useful for dosage prediction yet?Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011 Dec 1;50(12):759-72. doi: 10.2165/11596380-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011. PMID: 22087863 Review.
-
Effect of hypoalbuminemia on drug pharmacokinetics.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 20;16:1546465. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1546465. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40051558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinetic modelling of myocardial necrosis biomarkers offers an easier, reliable and more acceptable assessment of infarct size.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 12;10(1):13597. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70501-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32788683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Churg J, Habib R, White RHR. Pathology of nephrotic syndrome in children: a report for the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Lancet. 1970;760:1299–302. - PubMed
-
- Cattran DC, Alexopoulos E, Heering P, Hoyer PF, Johnston A, Meyrier A, Ponticelli C, Saito T, Choukroun G, Nachman P, Praga M, Yoshikawa N. Cyclosporin in idiopathic glomerular disease associated with the nephrotic syndrome: workshop recommendations. Kidney Int. 2007;72:1429–47. - PubMed
-
- Hino S, Takemura T, Okada M, Murakami K, Yagi K, Fukushima K, Yoshioka K. Follow-up of children with nephrotic syndrome treated with a long-term moderate dose of cyclosporine. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;31:932–9. - PubMed
-
- Okada M, Hino S, Takemura T, Fukushima K, Yoshioka K. Cyclosporine therapy in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Clin Exp Nephrol. 1999;3:S34–9.
-
- Moudgil A, Bagga A, Jordan SC. Mycophenolate mofetil therapy in frequently relapsing steroid-dependent and steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome of childhood: current status and future directions. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005;20:1376–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

