Integrin expression and function in the response of primary culture hepatic stellate cells to connective tissue growth factor (CCN2)
- PMID: 20406330
- PMCID: PMC2912974
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01072.x
Integrin expression and function in the response of primary culture hepatic stellate cells to connective tissue growth factor (CCN2)
Abstract
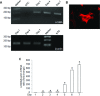
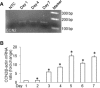
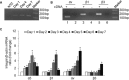
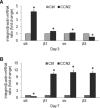
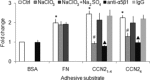
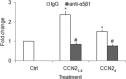
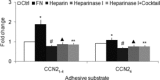
Production of connective tissue growth factor (CCN2, also known as CTGF) is a hallmark of hepatic fibrosis. This study examined early primary cultures of hepatic stellate cells (HSC) for (i) CCN2 regulation of its cognate receptor integrin subunits; and (ii) interactions between CCN2 and integrin α(5)β(1), heparan sulphate proteoglycans (HSPG) or fibronectin (FN) in supporting cell adhesion. HSC were isolated from healthy male Balb/c mice. mRNA levels of CCN2 or α(5), β(1), αv or β(3) integrin subunits were measured in days 1-7 primary culture HSC, and day 3 or day 7 cells treated with recombinant CCN2 or CCN2 small interfering RNA. Interactions between CCN2 and integrin α(5)β(1), HSPG or FN were investigated using an in vitro cell adhesion assay. Co-incident with autonomous activation over the first 7 days, primary culture HSC increasingly expressed mRNA for CCN2 or integrin subunits. Addition of exogenous CCN2 or knockdown of endogenous CCN2 differentially regulated integrin gene expression in day 3 versus day 7 cells. Either full length CCN2 ('CCN2(1-4)') or residues 247-349 containing module 4 alone ('CCN2(4)') supported day 3 cell adhesion in an integrin α(5)β(1) - and HSPG-dependent fashion. Adhesion of day 3 cells to FN was promoted in an integrin α(5) β(1)-dependent manner by CCN2(1-4) or CCN2(4), whereas FN promoted HSPG-dependent HSC adhesion to CCN2(1-4) or CCN2(4). These findings suggest CCN2 regulates integrin expression in primary culture HSC and supports HSC adhesion via its binding of cell surface integrin α(5)β(1), a novel CCN2 receptor in primary culture HSC which interacts co-operatively with HSPG or FN.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Iredale J. Defining therapeutic targets for liver fibrosis: exploiting the biology of inflammation and repair. Pharmacol Res. 2008;58:129–36. - PubMed
-
- Friedman SL. Stellate cells: a moving target in hepatic fibrogenesis. Hepatology. 2004;40:1041–3. - PubMed
-
- Reeves HL, Friedman SL. Activation of hepatic stellate cells–a key issue in liver fibrosis. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d808–26. - PubMed
-
- Rachfal AW, Brigstock DR. Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatol Res. 2003;26:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

