Clinicopathological parameters, recurrence, locoregional and distant metastasis in 115 T1-T2 oral squamous cell carcinoma patients
- PMID: 20406474
- PMCID: PMC2882907
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-3284-2-9
Clinicopathological parameters, recurrence, locoregional and distant metastasis in 115 T1-T2 oral squamous cell carcinoma patients
Abstract
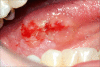
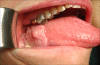
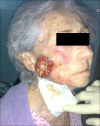
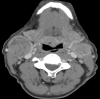
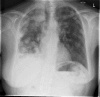
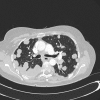
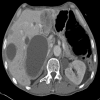
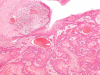
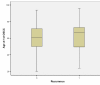
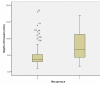
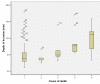
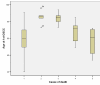
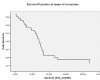
The incidence of oral squamous cell carcinoma remains high. Oral and oro-pharyngeal carcinomas are the sixth most common cancer in the world. Several clinicopathological parameters have been implicated in prognosis, recurrence and survival, following oral squamous cell carcinoma. In this retrospective analysis, clinicopathological parameters of 115 T1/T2 OSCC were studied and compared to recurrence and death from tumour-related causes. The study protocol was approved by the Joint UCL/UCLH committees of the ethics for human research. The patients' data was entered onto proformas, which were validated and checked by interval sampling. The fields included a range of clinical, operative and histopathological variables related to the status of the surgical margins. Data collection also included recurrence, cause of death, date of death and last clinic review. Causes of death were collated in 4 categories (1) death from locoregional spread, (2) death from distant metastasis, (3) death from bronchopulmonary pneumonia, and (4) death from any non-tumour event that lead to cardiorespiratory failure. The patients' population comprised 65 males and 50 females. Their mean age at the 1st diagnosis of OSCC was 61.7 years. Two-thirds of the patients were Caucasians. Primary sites were mainly identified in the tongue, floor of mouth (FOM), buccal mucosa and alveolus. Most of the identified OSCCs were low-risk (T1N0 and T2N0). All patients underwent primary resection +/- neck dissection and reconstruction when necessary. Twenty-two patients needed adjuvant radiotherapy. Pathological analysis revealed that half of the patients had moderately differentiated OSCC. pTNM slightly differed from the cTNM and showed that 70.4% of the patients had low-risk OSCC. Tumour clearance was ultimately achieved in 107 patients. Follow-up resulted in a 3-year survival of 74.8% and a 5-year survival of 72.2%. Recurrence was identified in 23 males and 20 females. The mean age of 1st diagnosis of the recurrence group was 59.53 years. Most common oral sites included the lateral border of tongue and floor of mouth. Recurrence was associated with clinical N-stage disease. The surgical margins in this group was evaluated and found that 17 had non-cohesive invasion, 30 had dysplasia at margin, 21 had vascular invasion, 9 had nerve invasion and 3 had bony invasion. Severe dysplasia was present in 37 patients. Tumour clearance was achieved in only 8 patients. The mean depth of tumour invasion in the recurrence group was 7.6 mm.An interesting finding was that 5/11 patients who died of distant metastasis had their primary disease in the tongue. Nodal disease comparison showed that 8/10 patients who died of locoregional metastasis and 8/11 patients who died from distant metastasis had clinical nodal involvement. Comparing this to pathological nodal disease (pTNM) showed that 10/10 patients and 10/11 patients who died from locoregional and distant metastasis, respectively, had nodal disease. All patients who died from locoregional and distant metastasis were shown to have recurrence after the primary tumour resection. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity has a poor overall prognosis with a high tendency to recur at the primary site and extend to involve the cervical lymph nodes. Several clinicopathological parameters can be employed to assess outcome, recurrence and overall survival.
Figures

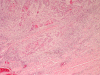
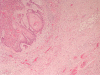

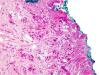
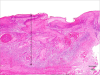
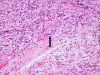
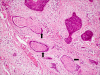
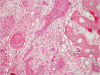
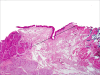
References
-
- Garzino-Demo P, Dell'Acqua A, Dalmasso P, Fasolis M, La Terra Maggiore GM, Ramieri G, Berrone S, Rampino M, Schena M. Clinicopathological parameters and outcome of 245 patients operated for oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2006;34(6):344–50. - PubMed
-
- Thames Cancer Registry. Cancer inequalities in London 2000-2004. London: TCR; 2007.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

