Structural determinants of allosteric agonism and modulation at the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor: identification of ligand-specific and global activation mechanisms
- PMID: 20406819
- PMCID: PMC2885178
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.125096
Structural determinants of allosteric agonism and modulation at the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor: identification of ligand-specific and global activation mechanisms
Abstract
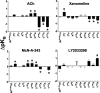
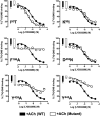
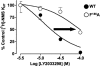
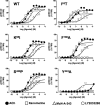
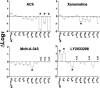
The recently identified small molecule, 3-amino-5-chloro-6-methoxy-4-methylthieno[2,3-b]pyridine-2-carboxylic acid cyclopropylamide (LY2033298), is the first selective allosteric modulator of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) that mediates both receptor activation and positive modulation of the endogenous agonist, acetylcholine (ACh), via the same allosteric site on the M(4) mAChR. We thus utilized this novel chemical tool, as well as ACh, the bitopic (orthosteric/allosteric) agonist, McN-A-343, and the clinically efficacious M(1)/M(4) mAChR-preferring agonist, xanomeline, in conjunction with site-directed mutagenesis of four different regions of the M(4) mAChR (extracellular loops 1, 2, and 3, and transmembrane domain 7), to identify regions that govern ligand-specific modes of binding, signaling, and allosteric modulation. In the first extracellular loop (E1), we identified Ile(93) and Lys(95) as key residues that specifically govern the signaling efficacy of LY2033298 and its binding cooperativity with ACh, whereas Phe(186) in the E2 loop was identified as a key contributor to the binding affinity of the modulator for the allosteric site, and Asp(432) in the E3 loop appears to be involved in the functional (activation) cooperativity between the modulator and the endogenous agonist. In contrast, the highly conserved transmembrane domain 7 residues, Tyr(439) and Tyr(443), were identified as contributing to a key activation switch utilized by all classes of agonists. These results provide new insights into the existence of multiple activation switches in G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), some of which can be selectively exploited by allosteric agonists, whereas others represent global activation mechanisms for all classes of ligand.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New insights into the function of M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors gained using a novel allosteric modulator and a DREADD (designer receptor exclusively activated by a designer drug).Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;74(4):1119-31. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.049353. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18628403
-
Impact of species variability and 'probe-dependence' on the detection and in vivo validation of allosteric modulation at the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;162(7):1659-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01184.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21198541 Free PMC article.
-
The role of transmembrane domain 3 in the actions of orthosteric, allosteric, and atypical agonists of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor.Mol Pharmacol. 2011 May;79(5):855-65. doi: 10.1124/mol.111.070938. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Mol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21300722
-
Discovery and Development of Muscarinic Acetylcholine M4 Activators as Promising Therapeutic Agents for CNS Diseases.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2018;66(1):37-44. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c17-00413. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2018. PMID: 29311510 Review.
-
The Prosperity and Adversity of M4 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Activators in the Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Disorders.J Med Chem. 2025 Apr 24;68(8):7932-7954. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c00678. Epub 2025 Apr 16. J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40237346 Review.
Cited by
-
Toward an understanding of the structural basis of allostery in muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.J Gen Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;150(10):1360-1372. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201711979. Epub 2018 Sep 6. J Gen Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30190312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular loop 2 of the free fatty acid receptor 2 mediates allosterism of a phenylacetamide ago-allosteric modulator.Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Jul;80(1):163-73. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.070789. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Mol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21498659 Free PMC article.
-
Fine Tuning Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Signaling Through Allostery and Bias.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 29;11:606656. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.606656. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33584282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xanomeline displays concomitant orthosteric and allosteric binding modes at the M4 mAChR.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 6;14(1):5440. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41199-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37673901 Free PMC article.
-
Motions around conserved helical weak spots facilitate GPCR activation.Proteins. 2021 Nov;89(11):1577-1586. doi: 10.1002/prot.26179. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Proteins. 2021. PMID: 34272892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harmar A. J., Hills R. A., Rosser E. M., Jones M., Buneman O. P., Dunbar D. R., Greenhill S. D., Hale V. A., Sharman J. L., Bonner T. I., Catterall W. A., Davenport A. P., Delagrange P., Dollery C. T., Foord S. M., Gutman G. A., Laudet V., Neubig R. R., Ohlstein E. H., Olsen R. W., Peters J., Pin J. P., Ruffolo R. R., Searls D. B., Wright M. W., Spedding M. (2009) Nucleic Acids Res. 37, D680–D685 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ballesteros J. A., Weinstein H. (1995) Methods Neurosci. 25, 366–428
-
- Hulme E. C., Lu Z. L., Saldanha J. W., Bee M. S. (2003) Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31, 29–34 - PubMed
-
- Lu Z. L., Saldanha J. W., Hulme E. C. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 34098–34104 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

