New strategies in head and neck cancer: understanding resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors
- PMID: 20406834
- PMCID: PMC2887084
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2318
New strategies in head and neck cancer: understanding resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors
Abstract
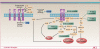
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a validated target in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC). However, despite high expression of EGFR in these cancers, EGFR inhibitor monotherapy has only had modest activity. Potential mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies involve EGFR and Ras mutations, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and activation of alternative and downstream pathways. Strategies to optimize EGFR-targeted therapy in head and neck cancer involve not only the selection for patients most likely to benefit but also the use of combination therapies to target the network of pathways involved in tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
Copyright 2010 AACR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small interfering RNA targeting epidermal growth factor receptor enhances chemosensitivity to cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil and docetaxel in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2006 Oct;97(10):1115-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00287.x. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16984384 Free PMC article.
-
Novel EGFR ectodomain mutations associated with ligand-independent activation and cetuximab resistance in head and neck cancer.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 18;15(2):e0229077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229077. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32069320 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphotoxin-β Interacts with Methylated EGFR to Mediate Acquired Resistance to Cetuximab in Head and Neck Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 1;23(15):4388-4401. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1955. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28196873
-
Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: focus on potential molecular mechanisms of drug resistance.Oncologist. 2013;18(7):850-64. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0013. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Oncologist. 2013. PMID: 23821327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: molecular bases for EGFR-targeted therapy.Pathol Res Pract. 2011 Jun 15;207(6):337-42. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2011.03.002. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2011. PMID: 21531084 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidermal growth factor signaling in transformed cells.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015;314:1-41. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2014.10.001. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25619714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoregulatory Potential of Exosomes Derived from Cancer Stem Cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2020 Mar 15;29(6):327-335. doi: 10.1089/scd.2019.0197. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Stem Cells Dev. 2020. PMID: 31856674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Major Molecular Signaling Pathways in Oral Cancer Associated With Therapeutic Resistance.Front Oral Health. 2021 Jan 25;1:603160. doi: 10.3389/froh.2020.603160. eCollection 2020. Front Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 35047986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-content pSTAT3/1 imaging assays to screen for selective inhibitors of STAT3 pathway activation in head and neck cancer cell lines.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2014 Jan-Feb;12(1):55-79. doi: 10.1089/adt.2013.524. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2014. PMID: 24127660 Free PMC article.
-
PIK3CA hotspot mutations differentially impact responses to MET targeting in MET-driven and non-driven preclinical cancer models.Mol Cancer. 2017 May 22;16(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0660-5. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28532501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ciardiello F, Tortora G. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) as a target in cancer therapy: understanding the role of receptor expression and other molecular determinants that could influence the response to anti-EGFR drugs. Eur J Cancer. 2003 Jul;39(10):1348–54. - PubMed
-
- Bonner JA, Raisch KP, Trummell HQ, Robert F, Meredith RF, Spencer SA, et al. Enhanced apoptosis with combination C225/radiation treatment serves as the impetus for clinical investigation in head and neck cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2000 Nov 1;18(21 Suppl):47S–53S. - PubMed
-
- Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2006 Feb 9;354(6):567–78. - PubMed
-
- Pollack VA, Savage DM, Baker DA, Tsaparikos KE, Sloan DE, Moyer JD, et al. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor-associated tyrosine phosphorylation in human carcinomas with CP-358,774: dynamics of receptor inhibition in situ and antitumor effects in athymic mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Nov;291(2):739–48. - PubMed
-
- Burtness B, Goldwasser MA, Flood W, Mattar B, Forastiere AA. Phase III randomized trial of cisplatin plus placebo compared with cisplatin plus cetuximab in metastatic/recurrent head and neck cancer: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2005 Dec 1;23(34):8646–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

