PAK4: a pluripotent kinase that regulates prostate cancer cell adhesion
- PMID: 20406887
- PMCID: PMC2864712
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.055707
PAK4: a pluripotent kinase that regulates prostate cancer cell adhesion
Abstract
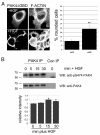
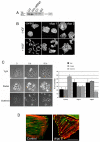
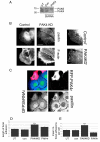
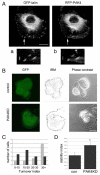
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is associated with tumour progression and increases the invasiveness of prostate carcinoma cells. Migration and invasion require coordinated reorganisation of the actin cytoskeleton and regulation of cell-adhesion dynamics. Rho-family GTPases orchestrate both of these cellular processes. p21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4), a specific effector of the Rho GTPase Cdc42, is activated by HGF, and we have previously shown that activated PAK4 induces a loss of both actin stress fibres and focal adhesions. We now report that DU145 human prostate cancer cells with reduced levels of PAK4 expression are unable to successfully migrate in response to HGF, have prominent actin stress fibres, and an increase in the size and number of focal adhesions. Moreover, these cells have a concomitant reduction in cell-adhesion turnover rates. We find that PAK4 is localised at focal adhesions, is immunoprecipitated with paxillin and phosphorylates paxillin on serine 272. Furthermore, we demonstrate that PAK4 can regulate RhoA activity via GEF-H1. Our results suggest that PAK4 is a pluripotent kinase that can regulate both actin cytoskeletal rearrangement and focal-adhesion dynamics.
Figures
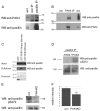
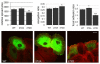
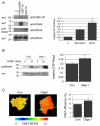
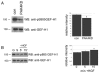

References
-
- Ahmed T., Shea K., Masters J. R. W., Jones G. E., Wells C. M. (2008). A PAK4-LIMK1 pathway drives prostate cancer cell migration downstream of HGF. Cell. Signal. 20, 1320-1328 - PubMed
-
- Arias-Romero L. E., Chernoff J. (2008). A tale of two Paks. Biol. Cell 100, 97-108 - PubMed
-
- Bailly M., Jones G. E. (2003). Polarised migration: cofilin holds the front. Curr. Biol. 13, R128-R130 - PubMed
-
- Barac A., Basile J., Vazquez-Prado J., Gao Y., Zheng Y., Gutkind J. S. (2004). Direct interaction of p21-activated kinase 4 with PDZ-RhoGEF, a G protein-linked Rho guanine exchange factor. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 6182-6189 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

