X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein inhibits apoptosis in inflammatory breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to an ErbB1/2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- PMID: 20406946
- PMCID: PMC2957814
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0160
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein inhibits apoptosis in inflammatory breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to an ErbB1/2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Abstract
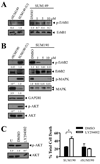
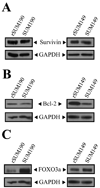
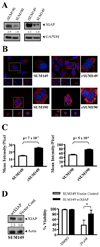
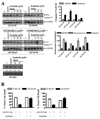
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a highly aggressive subtype of breast cancer that is often characterized by ErbB2 overexpression. ErbB2 targeting is clinically relevant using trastuzumab (anti-ErbB2 antibody) and lapatinib (small-molecule ErbB1/2 inhibitor). However, acquired resistance is a common outcome even in IBC patients who show an initial clinical response, which limits the efficacy of these agents. In the present study, using a clonal population of GW583340 (lapatinib analogue, ErbB1/2 inhibitor)-resistant IBC cells, we identified the overexpression of an antiapoptotic protein, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), in acquired resistance to GW583340 in both ErbB2-overexpressing SUM190 and ErbB1-activated SUM149 cell lines derived from primary IBC tumors. A marked decrease in p-ErbB2, p-ErbB1, and downstream signaling was evident in the GW583340-resistant cells (rSUM190 and rSUM149) similar to parental counterparts treated with the drug, suggesting that the primary mechanism of action of GW583340 was not compromised in resistant cells. However, rSUM190 and rSUM149 cells growing in GW583340 had significant XIAP overexpression and resistance to GW583340-mediated apoptosis. Additionally, stable XIAP overexpression using a lentiviral system reversed sensitivity to GW583340 in parental cells. The observed overexpression was identified to be caused by IRES-mediated XIAP translation. XIAP downregulation in rSUM190 and rSUM149 cells using a small-molecule inhibitor (embelin), which abrogates the XIAP/procaspase-9 interaction, resulted in decreased viability, showing that XIAP is required for survival of cells with acquired resistance to GW583340. These studies establish the feasibility of development of an XIAP inhibitor that potentiates apoptosis for use in IBC patients with resistance to ErbB2-targeting agents.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ErbB1/2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor mediates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in inflammatory breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Feb;132(1):109-19. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1568-1. Epub 2011 May 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21559822 Free PMC article.
-
Trastuzumab signaling in ErbB2-overexpressing inflammatory breast cancer correlates with X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein expression.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Jan;7(1):38-47. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0370. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18202008
-
XIAP inhibition and generation of reactive oxygen species enhances TRAIL sensitivity in inflammatory breast cancer cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Jul;11(7):1518-27. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0787. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22508521
-
Acquired resistance to small molecule ErbB2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 1;14(21):6730-4. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0581. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18980964 Review.
-
Does lapatinib, a small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor, constitute a breakthrough in the treatment of breast cancer?Breast Cancer. 2007;14(2):156-62. doi: 10.2325/jbcs.971. Breast Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17485900 Review.
Cited by
-
HER2-targeted therapies for HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer: present and future.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 16;15:1446414. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1446414. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39351085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photothermal ablation of inflammatory breast cancer tumor emboli using plasmonic gold nanostars.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Aug 26;12:6259-6272. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S141164. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28894365 Free PMC article.
-
Lapatinib resistance in HER2+ cancers: latest findings and new concepts on molecular mechanisms.Tumour Biol. 2016 Dec;37:15411–15431. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5467-2. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27726101 Review.
-
Adaptive stress response genes associated with breast cancer subtypes and survival outcomes reveal race-related differences.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022 Jun 13;8(1):73. doi: 10.1038/s41523-022-00431-z. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35697736 Free PMC article.
-
XIAP Regulation by MNK Links MAPK and NFκB Signaling to Determine an Aggressive Breast Cancer Phenotype.Cancer Res. 2018 Apr 1;78(7):1726-1738. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1667. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29351901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evan GI, Vousden KH. Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 2001;411:342–348. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Hunter AM, LaCasse EC, Korneluk RG. The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) as cancer targets. Apoptosis. 2007;12:1543–1568. - PubMed
-
- Deveraux QL, Reed JC. IAP family proteins--suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999;13:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Liston P, Fong WG, Korneluk RG. The inhibitors of apoptosis: there is more to life than Bcl2. Oncogene. 2003;22:8568–8580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

