Requirement of the NF-kappaB subunit p65/RelA for K-Ras-induced lung tumorigenesis
- PMID: 20406971
- PMCID: PMC2862109
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4290
Requirement of the NF-kappaB subunit p65/RelA for K-Ras-induced lung tumorigenesis
Abstract
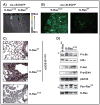
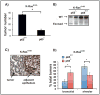
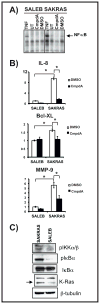
K-Ras-induced lung cancer is a very common disease, for which there are currently no effective therapies. Because therapy directly targeting the activity of oncogenic Ras has been unsuccessful, a different approach for novel therapy design is to identify critical Ras downstream oncogenic targets. Given that oncogenic Ras proteins activate the transcription factor NF-kappaB, and the importance of NF-kappaB in oncogenesis, we hypothesized that NF-kappaB would be an important K-Ras target in lung cancer. To address this hypothesis, we generated a NF-kappaB-EGFP reporter mouse model of K-Ras-induced lung cancer and determined that K-Ras activates NF-kappaB in lung tumors in situ. Furthermore, a mouse model was generated where activation of oncogenic K-Ras in lung cells was coupled with inactivation of the NF-kappaB subunit p65/RelA. In this model, deletion of p65/RelA reduces the number of K-Ras-induced lung tumors both in the presence and in the absence of the tumor suppressor p53. Lung tumors with loss of p65/RelA have higher numbers of apoptotic cells, reduced spread, and lower grade. Using lung cell lines expressing oncogenic K-Ras, we show that NF-kappaB is activated in these cells in a K-Ras-dependent manner and that NF-kappaB activation by K-Ras requires inhibitor of kappaB kinase beta (IKKbeta) kinase activity. Taken together, these results show the importance of the NF-kappaB subunit p65/RelA in K-Ras-induced lung transformation and identify IKKbeta as a potential therapeutic target for K-Ras-induced lung cancer.
(c)2010 AACR.
Figures

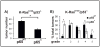

References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer Statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49. - PubMed
-
- Mills NE, Fishman CL, Rom WN, Dubin N, Jacobson DR. Increased Prevalence of K-ras Oncogene Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1995;55:1444–7. - PubMed
-
- Rodenhuis S, Slebos RJ. Clinical significance of ras oncogene activation in human lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1992;52:2665s–9s. - PubMed
-
- Slebos RJ, Rodenhuis S. The ras gene family in human non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1992:23–9. - PubMed
-
- Graziano SL, Gamble GP, Newman NB, Abbott LZ, Rooney M, Mookherjee S, et al. Prognostic Significance of K-ras Codon 12 Mutations in Patients With Resected Stage I and II Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

