Mechanism of autophagy to apoptosis switch triggered in prostate cancer cells by antitumor cytokine melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7/interleukin-24
- PMID: 20406981
- PMCID: PMC2874885
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3647
Mechanism of autophagy to apoptosis switch triggered in prostate cancer cells by antitumor cytokine melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7/interleukin-24
Abstract
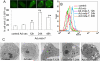
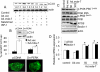
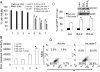
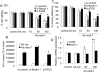
Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7 (mda-7)/interleukin-24 (IL-24) is a unique member of the IL-10 gene family, which displays a broad range of antitumor properties, including induction of cancer-specific apoptosis. Adenoviral-mediated delivery by Ad.mda-7 invokes an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response that is associated with ceramide production and autophagy in some cancer cells. Here, we report that Ad.mda-7-induced ER stress and ceramide production trigger autophagy in human prostate cancer cells, but not in normal prostate epithelial cells, through a canonical signaling pathway that involves Beclin-1, atg5, and hVps34. Autophagy occurs in cancer cells at early times after Ad.mda-7 infection, but a switch to apoptosis occurs by 48 hours after infection. Inhibiting autophagy with 3-methyladenosine increases Ad.mda-7-induced apoptosis, suggesting that autophagy may be initiated first as a cytoprotective mechanism. Inhibiting apoptosis by overexpression of antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL increased autophagy after Ad.mda-7 infection. During the apoptotic phase, the MDA-7/IL-24 protein physically interacted with Beclin-1 in a manner that could inhibit Beclin-1 function culminating in apoptosis. Conversely, Ad.mda-7 infection elicited calpain-mediated cleavage of the autophagic protein ATG5 in a manner that could facilitate switch to apoptosis. Our findings reveal novel aspects of the interplay between autophagy and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells that underlie the cytotoxic action of mda-7/IL-24, possibly providing new insights in the development of combinatorial therapies for prostate cancer.
(c)2010 AACR.
Figures

References
-
- Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene. 1995;11:2477–86. - PubMed
-
- Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Sarkar D, et al. MDA-7/IL-24: novel cancer growth suppressing and apoptosis inducing cytokine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14:35–51. - PubMed
-
- Pestka S, Krause CD, Sarkar D, Walter MR, Shi Y, Fisher PB. Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:929–79. - PubMed
-
- Fisher PB, Gopalkrishnan RV, Chada S, et al. mda7-7/IL-24, a novel cancer selective apoptosis inducing cytokine gene: from the laboratory into the clinic. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003;2:S23–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

