Loss of p130 accelerates tumor development in a mouse model for human small-cell lung carcinoma
- PMID: 20406986
- PMCID: PMC2873158
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4228
Loss of p130 accelerates tumor development in a mouse model for human small-cell lung carcinoma
Abstract
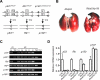
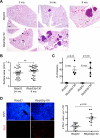
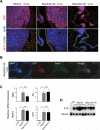
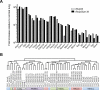
Small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) is a neuroendocrine subtype of lung cancer. Although SCLC patients often initially respond to therapy, tumors nearly always recur, resulting in a 5-year survival rate of less than 10%. A mouse model has been developed based on the fact that the RB and p53 tumor suppressor genes are mutated in more than 90% of human SCLCs. Emerging evidence in patients and mouse models suggests that p130, a gene related to RB, may act as a tumor suppressor in SCLC cells. To test this idea, we used conditional mutant mice to delete p130 in combination with Rb and p53 in adult lung epithelial cells. We found that loss of p130 resulted in increased proliferation and significant acceleration of SCLC development in this triple-knockout mouse model. The histopathologic features of the triple-mutant mouse tumors closely resembled that of human SCLC. Genome-wide expression profiling experiments further showed that Rb/p53/p130-mutant mouse tumors were similar to human SCLC. These findings indicate that p130 plays a key tumor suppressor role in SCLC. Rb/p53/p130-mutant mice provide a novel preclinical mouse model to identify novel therapeutic targets against SCLC.
(c)2010 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Meuwissen R, Linn SC, Linnoila RI, Zevenhoven J, Mooi WJ, Berns A. Induction of small cell lung cancer by somatic inactivation of both Trp53 and Rb1 in a conditional mouse model. Cancer Cell. 2003;4:181–9. - PubMed
-
- Wistuba II, Gazdar AF, Minna JD. Molecular genetics of small cell lung carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 2001;28:3–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

