Role of N-linked glycosylation in biosynthesis, trafficking, and function of the human glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor
- PMID: 20407008
- PMCID: PMC2904048
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00067.2010
Role of N-linked glycosylation in biosynthesis, trafficking, and function of the human glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor
Abstract
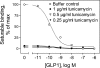
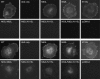
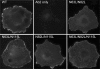
The family B G protein-coupled glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor is an important drug target for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Like other family members, the GLP-1 receptor is a glycosylated membrane protein that contains three potential sites for N-linked glycosylation within the functionally important extracellular amino-terminal domain. However, the roles for each potential site of glycosylation in receptor biosynthesis, trafficking, and function are not known. In this work, we demonstrated that tunicamycin inhibition of glycosylation of the GLP-1 receptor expressed in CHO cells interfered with biosynthesis and intracellular trafficking, thereby eliminating natural ligand binding. To further investigate the roles of each of the glycosylation sites, site-directed mutagenesis was performed to eliminate these sites individually and in aggregate. Our results showed that mutation of each of the glycosylation sites individually did not interfere with receptor expression on the cell surface, ligand binding, and biological activity. However, simultaneous mutation of two or three glycosylation sites resulted in almost complete loss of GLP-1 binding and severely impaired biological activity. Immunostaining studies demonstrated receptor biosynthesis but aberrant trafficking, with most of the receptor trapped in the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi compartments and little of the receptor expressed on the cell surface. Interestingly, surface expression, ligand binding, and biological activity of these mutants improved significantly when biosynthesis was slowed using low temperature (30 degrees C). These data suggest that N-linked glycosylation of the GLP-1 receptor is important for its normal folding and trafficking to the cell surface.
Figures
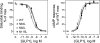
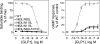
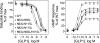
Similar articles
-
Structural Determinants of Binding the Seven-transmembrane Domain of the Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor (GLP-1R).J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 17;291(25):12991-3004. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.721977. Epub 2016 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27059958 Free PMC article.
-
N-Glycosylation of the human kappa opioid receptor enhances its stability but slows its trafficking along the biosynthesis pathway.Biochemistry. 2007 Sep 25;46(38):10960-70. doi: 10.1021/bi700443j. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17711303
-
Identification of the sites of N-linked glycosylation on the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) receptor and assessment of their role in FSH receptor function.Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Feb;9(2):159-70. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.2.7776966. Mol Endocrinol. 1995. PMID: 7776966
-
Glycosylation of the GLP-1 receptor is a prerequisite for regular receptor function.Peptides. 1994;15(4):675-81. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)90095-7. Peptides. 1994. PMID: 7937345
-
Structural and functional analysis of the canine histamine H2 receptor by site-directed mutagenesis: N-glycosylation is not vital for its action.Biochem J. 1995 Sep 1;310 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):553-8. doi: 10.1042/bj3100553. Biochem J. 1995. PMID: 7544576 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists in Hypoglycemia.Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021 Oct 17;14:11795514211051697. doi: 10.1177/11795514211051697. eCollection 2021. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34690504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid One-Step Capturing of Native, Cell-Free Synthesized and Membrane-Embedded GLP-1R.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 1;24(3):2808. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032808. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769142 Free PMC article.
-
Calcitonin Receptor N-Glycosylation Enhances Peptide Hormone Affinity by Controlling Receptor Dynamics.J Mol Biol. 2020 Mar 27;432(7):1996-2014. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.01.028. Epub 2020 Feb 6. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32035902 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized protocol for expression and purification of membrane-bound PglB, a bacterial oligosaccharyl transferase.Protein Expr Purif. 2013 Jun;89(2):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Protein Expr Purif. 2013. PMID: 23583934 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant expression, purification, and functional characterisation of connective tissue growth factor and nephroblastoma-overexpressed protein.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 30;5(12):e16000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016000. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21209863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anukanth A, Khorana HG. Structure and function in rhodopsin. Requirements of a specific structure for the intradiscal domain. J Biol Chem 269: 19738–19744, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Assil IQ, Abou-Samra AB. N-glycosylation of CRF receptor type 1 is important for its ligand-specific interaction. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 281: E1015–E1021, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Bisello A, Greenberg Z, Behar V, Rosenblatt M, Suva LJ, Chorev M. Role of glycosylation in expression and function of the human parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor. Biochemistry 35: 15890–15895, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Breitfeld PP, Rup D, Schwartz AL. Influence of the N-linked oligosaccharides on the biosynthesis, intracellular routing, and function of the human asialoglycoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem 259: 10414–10421, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Buhlmann N, Aldecoa A, Leuthauser K, Gujer R, Muff R, Fischer JA, Born W. Glycosylation of the calcitonin receptor-like receptor at Asn(60) or Asn(112) is important for cell surface expression. FEBS Lett 486: 320–324, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

