Engineering of human pluripotent stem cells by AAV-mediated gene targeting
- PMID: 20407427
- PMCID: PMC2889726
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2010.55
Engineering of human pluripotent stem cells by AAV-mediated gene targeting
Abstract
Precise genetic manipulation of human pluripotent stem cells will be required to realize their scientific and therapeutic potential. Here, we show that adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene targeting vectors can be used to genetically engineer human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Different types of sequence-specific changes, including the creation and correction of mutations, were introduced into the human HPRT1 and HMGA1 genes (HPRT1 mutations being responsible for Lesch-Nyhan syndrome). Gene targeting occurred at high frequencies in both ESCs and iPSCs, with over 1% of all colony-forming units (CFUs) undergoing targeting in some experiments. AAV vectors could also be used to target genes in human fibroblasts that were subsequently used to derive iPSCs. Accurate and efficient targeting took place with minimal or no cytotoxicity, and most of the gene-targeted stem cells produced were euploid and pluripotent.
Figures

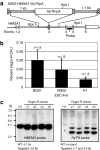
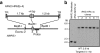



Comment in
-
Gene correction in human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells: promises and challenges ahead.Mol Ther. 2010 Jun;18(6):1061-3. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.92. Mol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20514030 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Gene targeting in human pluripotent stem cells with adeno-associated virus vectors.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Oct 30;388(4):711-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.075. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19695233
-
Enhanced gene targeting of adult and pluripotent stem cells using evolved adeno-associated virus.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1114:169-79. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-761-7_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24557903
-
Directed evolution of adeno-associated virus for enhanced gene delivery and gene targeting in human pluripotent stem cells.Mol Ther. 2012 Feb;20(2):329-38. doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.255. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Mol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22108859 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor targeting of adeno-associated virus vectors.Gene Ther. 2003 Jul;10(14):1142-51. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3301976. Gene Ther. 2003. PMID: 12833123 Review.
-
Find and replace: editing human genome in pluripotent stem cells.Protein Cell. 2011 Dec;2(12):950-6. doi: 10.1007/s13238-011-1132-0. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Protein Cell. 2011. PMID: 22173708 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Concise review: Human cell engineering: cellular reprogramming and genome editing.Stem Cells. 2012 Jan;30(1):75-81. doi: 10.1002/stem.735. Stem Cells. 2012. PMID: 21905170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inborn errors of metabolism: Lessons from iPSC models.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021 Dec;22(4):1189-1200. doi: 10.1007/s11154-021-09671-z. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 34241766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome Editing for the Study of Cardiovascular Diseases.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2017 Mar;19(3):22. doi: 10.1007/s11886-017-0830-5. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28220462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration-defective lentiviral vector mediates efficient gene editing through homology-directed repair in human embryonic stem cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Mar 17;45(5):e29. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1057. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899664 Free PMC article.
-
Normal collagen and bone production by gene-targeted human osteogenesis imperfecta iPSCs.Mol Ther. 2012 Jan;20(1):204-13. doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.209. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Mol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22031238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318:1917–1920. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Di Domenico AI, Christodoulou I, Pells SC, McWhir J., and , Thomson AJ. Sequential genetic modification of the hprt locus in human ESCs combining gene targeting and recombinase-mediated cassette exchange. Cloning Stem Cells. 2008;10:217–230. - PubMed
-
- Draper JS, Smith K, Gokhale P, Moore HD, Maltby E, Johnson J, et al. Recurrent gain of chromosomes 17q and 12 in cultured human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22:53–54. - PubMed
-
- Urbach A, Schuldiner M., and , Benvenisty N. Modeling for Lesch-Nyhan disease by gene targeting in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22:635–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

