MRI estimation of global brain oxygen consumption rate
- PMID: 20407465
- PMCID: PMC2949253
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.49
MRI estimation of global brain oxygen consumption rate
Erratum in
- J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010 Dec;30(12):1987
- J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011 May;31(5):1336
Abstract
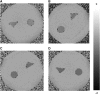
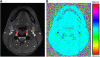
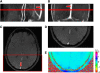
Measuring the global cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO(2)) is a valuable tool for assessing brain vitality and function. Measurement of blood oxygen saturation (HbO(2)) and flow in the major cerebral outflow and inflow vessels can provide a global estimate of CMRO(2). We demonstrate a rapid noninvasive method for quantifying CMRO(2) by simultaneously measuring venous oxygen saturation in the superior sagittal sinus with magnetic resonance susceptometry-based oximetry, a technique that exploits the intrinsic susceptibility of deoxygenated hemoglobin, and the average blood inflow rate with phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. The average venous HbO(2), cerebral blood flow, and global CMRO(2) values in eight healthy, normal study subjects were 64%+/-4%, 45.2+/-3.2 mL per 100 g per minute, and 127+/-7 micromol per 100 g per minute, respectively. These values are in good agreement with those reported in literature. The technique described is noninvasive, robust, and reproducible for in vivo applications, making it ideal for use in clinical settings for assessing the pathologies associated with dysregulation of cerebral metabolism. In addition, the short acquisition time (approximately 30 seconds) makes the technique suitable for studying the temporal variations in CMRO(2) in response to physiologic challenges.
Figures
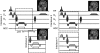

References
-
- Abduljalil AM, Schmalbrock P, Novak V, Chakeres DW. Enhanced gray and white matter contrast of phase susceptibility-weighted images in ultra-high-field magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2003;18:284–290. - PubMed
-
- An H, Lin W. Impact of intravascular signal on quantitative measures of cerebral oxygen extraction and blood volume under normo- and hypercapnic conditions using an asymmetric spin echo approach. Magn Reson Med. 2003;50:708–716. - PubMed
-
- Bryant DJ, Payne JA, Firmin DN, Longmore DB. Measurement of flow with NMR imaging using a gradient pulse and phase difference technique. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984;8:588–593. - PubMed
-
- Chien D, Levin DL, Anderson CM. MR gradient echo imaging of intravascular blood oxygenation: T2* determination in the presence of flow. Magn Reson Med. 1994;32:540–545. - PubMed
-
- Coles JP, Minhas PS, Fryer TD, Smielewski P, Aigbirihio F, Donovan T, Downey SP, Williams G, Chatfield D, Matthews JC, Gupta AK, Carpenter TA, Clark JC, Pickard JD, Menon DK. Effect of hyperventilation on cerebral blood flow in traumatic head injury: clinical relevance and monitoring correlates. Crit Care Med. 2002;30:1950–1959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

