Blood flow interplays with elastin: collagen and MMP: TIMP ratios to maintain healthy vascular structure and function
- PMID: 20407629
- PMCID: PMC2856577
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s9472
Blood flow interplays with elastin: collagen and MMP: TIMP ratios to maintain healthy vascular structure and function
Abstract
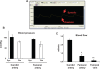
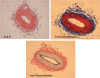
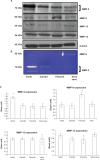
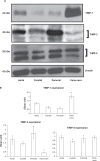
Differential vascular remodeling is one of the major mechanisms of heterogeneity in atherosclerosis. The structural and functional heterogeneity between arteries and veins determines the degree of vascular remodeling. Matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) play key roles in vascular structural and functional remodeling. We hypothesized that the level of blood flow in different arteries and veins caused structural and functional heterogeneity that ultimately determined potential vascular remodeling. To test this hypothesis, in vivo blood flow and blood pressure in the aorta, carotid, femoral artery, and femoral vein was measured in male Sprague-Dawley rats (weight 380-400 gm). Arterial and venous pressures were measured by PE-50 catheter cannulation. Blood flow was measured by a transonic ultrasound system. The aortic arch, femoral and carotid arteries, and abdominal vena cava were isolated to determine the expression of MMP-2, -9, -12, and -13 and TIMP-1, -3, and -4 by Western blot and in gelatin gel zymography. Masson trichrome and van Gieson stains were used to stain the histologic tissue sections. The results revealed that blood flow was higher in the aorta and carotid artery than the femoral artery and vein. MMP-9 and MMP-13 were higher in the carotid artery in comparison with the other blood vessels, while TIMP-3 showed higher expression in the aorta than the arteries. Further, the MMP-9 activity was significantly higher in the carotid artery than in the aorta and femoral artery. There was a higher degree of basement membrane collagen in the femoral artery and therefore a low elastin: collagen ratio, while in the carotid artery a higher level of elastin and, therefore, a high elastin: collagen ratio was found. The results suggested that medial thickness and elastin:collagen ratios had a threshold in blood flow in the range 0.6-2.5 mL/min, which increased robustly if blood flow increased to 2.7 mL/min. This pattern was inverted by the total MMP:TIMP ratio. We conclude that vascular remodeling is a function of rate of blood flow, which would in turn be determined by the amounts of MMPs and their inhibitors present. The study combined the endothelial and dynamic (blood flow/pressure) components that affect medial thickness and elastin: collagen ratios.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; passive stretch-tension relationship; vascular remodeling.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Reduced NO signaling during pregnancy attenuates outward uterine artery remodeling by altering MMP expression and collagen and elastin deposition.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Oct;301(4):H1266-75. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00519.2011. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21856919 Free PMC article.
-
Functional consequences of the collagen/elastin switch in vascular remodeling in hyperhomocysteinemic wild-type, eNOS-/-, and iNOS-/- mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 Sep;299(3):L301-11. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00065.2010. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20581102 Free PMC article.
-
Homocysteine decreases blood flow to the brain due to vascular resistance in carotid artery.Neurochem Int. 2008 Dec;53(6-8):214-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.07.008. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Neurochem Int. 2008. PMID: 18725259 Free PMC article.
-
An alternate perspective on the roles of TIMPs and MMPs in pathology.Am J Pathol. 2012 Jan;180(1):12-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.09.008. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Am J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22033229 Review.
-
Importance of plasma matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMP) in development of fibrosis in agnogenic myeloid metaplasia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2005 Sep;46(9):1261-8. doi: 10.1080/10428190500126463. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005. PMID: 16109602 Review.
Cited by
-
Building a Scaffold for Arteriovenous Fistula Maturation: Unravelling the Role of the Extracellular Matrix.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 28;24(13):10825. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310825. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between promoters polymorphisms of matrix metalloproteinases and risk of digestive cancers: a meta-analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013 Sep;139(9):1433-47. doi: 10.1007/s00432-013-1446-9. Epub 2013 May 5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23644699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remodeling in vein expresses arterial phenotype in hyperhomocysteinemia.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2011;3(4):266-79. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22162783 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases are possible targets in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension: investigation of anti-remodeling effects of alagebrium and everolimus.Anatol J Cardiol. 2017 Jan;17(1):8-17. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2016.6891. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Anatol J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27182612 Free PMC article.
-
Time-dependent alterations in rat macrovessels with type 1 diabetes.Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2012:278620. doi: 10.1155/2012/278620. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012. PMID: 22315586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenwald SE. Ageing of the conduit arteries. J Pathol. 2007;211(2):157–172. - PubMed
-
- Milewicz DM, Urban Z, Boyd C. Genetic disorders of the elastic fiber system. Matrix Biol. 2000;19(6):471–480. - PubMed
-
- Apter JT. Correlation of visco-elastic properties with microscopic structure of large arteries. IV. Thermal responses of collagen, elastin, smooth muscle, and intact arteries. Circ Res. 1996;21(6):901–918. - PubMed
-
- Harkness ML, Harkness RD, McDonald DA. The collagen and elastin content of the arterial wall in the dog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957;146(925):541–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

