Role of valsartan, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide fixed combination in blood pressure control: an update
- PMID: 20407632
- PMCID: PMC2856580
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s6805
Role of valsartan, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide fixed combination in blood pressure control: an update
Abstract
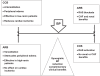
The treatment of moderate or severe hypertension in most cases requires the contemporaneous use of multiple antihypertensive agents. The most available two-drug combinations have an agent that addresses renin secretion and another one that is statistically more effective in renin-independent hypertension. The practice of combining agents that counteract different mechanisms is the most likely explanation for the fact that most available two-drug combinations have an agent that addresses renin secretion (beta-blocker, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin II receptor blocker or direct renin inhibitor) and another one that is more effective in renin-independent hypertension (diuretic, dihydropyridine or non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker). Based on these considerations, addition of hydrochlorothiazide to the combination of an antagonist of the renin-angiotensin system with a calcium channel blocker would constitute a logical approach. Inclusion of a diuretic in the triple combination is based on the evidence that these agents are effective and cheap, enhance the effect of other antihypertensive agents, and add a specific effect to individuals with salt-sensitivity of blood pressure. The benefit of triple combination therapy with amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide over its dual component therapies has been demonstrated, and the use of a single pill will simplify therapy resulting in better blood pressure control.
Keywords: HCTZ; amlodipine; blood pressure; hydrochlorothiazide; hypertension; valsartan.
Figures


References
-
- Kearney P, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton P, He J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian A, Bakris G, Black H. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- Wolf-Maier K, Cooper R, Kramer H, et al. Hypertension treatment and control in five European countries, Canada, and the United States. Hypertension. 2004;43:10–17. - PubMed
-
- Antikainen R, Moltchanov V, Chukwuma C, et al. Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension: The WHO MONICA Project. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2006;13:13–29. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. for ESH-ESC Task Force on the Management of Arterial Hypertension 2007 ESH-ESC practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens. 2007;25(9):1751–1762. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

