The Neuronal Splicing Factor Nova Co-Localizes with Target RNAs in the Dendrite
- PMID: 20407637
- PMCID: PMC2856630
- DOI: 10.3389/neuro.04.005.2010
The Neuronal Splicing Factor Nova Co-Localizes with Target RNAs in the Dendrite
Abstract
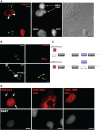
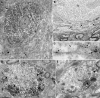
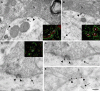
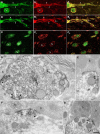
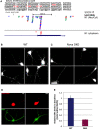
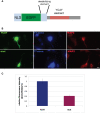
Nova proteins are neuron-specific RNA binding proteins targeted by autoantibodies in a disorder manifest by failure of motor inhibition, and they regulate splicing and alternative 3' processing. Nova regulates splicing of RNAs encoding synaptic proteins, including the inhibitory glycine receptor alpha2 subunit (GlyRalpha2), and binds to others, including the GIRK2 channel. We found that Nova harbors functional NES and NLS elements, shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm, and that 50% of the protein localizes to the soma-dendritic compartment. Immunofluoresence and EM analysis of spinal cord motor neurons demonstrated that Nova co-localizes beneath synaptic contacts in dendrites with the same RNA, GlyRalpha2, whose splicing it regulates in the nucleus. HITS-CLIP identified intronic and 3' UTR sites where Nova binds to GlyRalpha2 and GIRK2 transcripts in the brain. This led directly to the identification of a 3' UTR localization element that mediates Nova-dependent localization of GIRK2 in primary neurons. These data demonstrate that HITS-CLIP can identify functional RNA localization elements, and they suggest new links between the regulation of nuclear RNA processing and mRNA localization.
Keywords: GIRK2; HITS-CLIP; RNA localization; RNA splicing; glycine receptor; nova; shuttling protein; spinal motor neuron.
Figures


Similar articles
-
NOVA-dependent regulation of cryptic NMD exons controls synaptic protein levels after seizure.Elife. 2013 Jan 22;2:e00178. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00178. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23359859 Free PMC article.
-
Nova autoregulation reveals dual functions in neuronal splicing.EMBO J. 2005 Apr 20;24(8):1608-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600630. Epub 2005 Mar 31. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15933722 Free PMC article.
-
Nova-1 regulates neuron-specific alternative splicing and is essential for neuronal viability.Neuron. 2000 Feb;25(2):359-71. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80900-9. Neuron. 2000. PMID: 10719891
-
Alternative Splicing by NOVA Factors: From Gene Expression to Cell Physiology and Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 30;21(11):3941. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113941. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32486302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ELAV proteins along evolution: back to the nucleus?Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:447-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23439364 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic insights into the basis of widespread RNA localization.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Jul;26(7):1037-1046. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01444-5. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38956277 Review.
-
Gene Expression Profiles Controlled by the Alternative Splicing Factor Nova2 in Endothelial Cells.Cells. 2019 Nov 23;8(12):1498. doi: 10.3390/cells8121498. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31771184 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Inactivity Co-opts LTP Machinery to Drive Potassium Channel Splicing and Homeostatic Spike Widening.Cell. 2020 Jun 25;181(7):1547-1565.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.013. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32492405 Free PMC article.
-
RNA binding proteins: a common denominator of neuronal function and dysfunction.Neurosci Bull. 2014 Aug;30(4):610-26. doi: 10.1007/s12264-014-1443-7. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Neurosci Bull. 2014. PMID: 24962082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulated Intron Removal Integrates Motivational State and Experience.Cell. 2017 May 18;169(5):836-848.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.006. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28525754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassell G. J., Singer R. H. (2001). Neuronal RNA localization and the cytoskeleton. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 34, 41–56 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

