Neurotrophin-4 (ntf4) mediates neurogenesis in mouse embryonic neural stem cells through the inhibition of the signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (stat3) and the modulation of the activity of protein kinase B
- PMID: 20407817
- PMCID: PMC11498831
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-010-9520-1
Neurotrophin-4 (ntf4) mediates neurogenesis in mouse embryonic neural stem cells through the inhibition of the signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (stat3) and the modulation of the activity of protein kinase B
Abstract
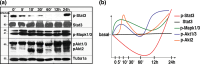
The effect of neurotrophin-4 (Ntf4) on mouse embryonic (day-14) neural stem cell (mE14-NSC) fate determination and the mechanisms involved were investigated. Using primary mE14-NSCs, immunocytochemistry and molecular-cell biological methods, such as Western-blotting, we characterized the effect of Ntf4 on mE14-NSC differentiation. Obtained in-vitro data revealed an interesting phenomenon of Ntf4 action resulting in enhanced mE14-NSC commitment to progenitor cells of the neuronal lineage. During this process, Ntf4 suppresses the interleukin 6 (Il6) family receptor and the Notch signalling pathways by modulating their specific receptor cleavages. The observed lineage commitment is controlled via an Ntf4-mediated modulation of protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) activity and characterized by a decreased Stat3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription-3) phosphorylation status. These findings suggest that the Ntf4-activated signalling cascade is responsible for initiating a concert among sheddases, kinases, and phosphatases to mediate neurogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lithium suppresses astrogliogenesis by neural stem and progenitor cells by inhibiting STAT3 pathway independently of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e23341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023341. Epub 2011 Sep 9. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21931595 Free PMC article.
-
Ionizing Radiation Induces Altered Neuronal Differentiation by mGluR1 through PI3K-STAT3 Signaling in C17.2 Mouse Neural Stem-Like Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 1;11(2):e0147538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147538. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26828720 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has proliferative effects on neural stem cells through the truncated TRK-B receptor, MAP kinase, AKT, and STAT-3 signaling pathways.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2009 Feb;6(1):42-53. doi: 10.2174/156720209787466028. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2009. PMID: 19355925
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 controls neural stem cell activation in mice and humans.Cell Rep. 2015 Feb 24;10(7):1158-72. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.01.049. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25704818 Free PMC article.
-
Immunopharmacological intervention for successful neural stem cell therapy: New perspectives in CNS neurogenesis and repair.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Jan;141(1):21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 23954656 Review.
Cited by
-
miRNAs stem cell reprogramming for neuronal induction and differentiation.Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Jun;43(3):215-27. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8179-z. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21541853 Review.
-
Neurotrophin Signaling and Stem Cells-Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases and Stem Cell Therapy.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Nov;54(9):7401-7459. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0214-7. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27815842 Review.
-
Exploration of the Immune-Related Signatures and Immune Infiltration Analysis in Melanoma.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021 Jan 16;2021:4743971. doi: 10.1155/2021/4743971. eCollection 2021. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021. PMID: 33511023 Free PMC article.
-
The Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Approaches of Diabetic Neuropathy in the Retina.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 22;22(16):9050. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169050. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain site-specific proteome changes in aging-related dementia.Exp Mol Med. 2013 Sep 6;45(9):e39. doi: 10.1038/emm.2013.76. Exp Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24008896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Althoff K, Reddy P, Voltz N, Rose-John S, Mullberg J (2000) Shedding of interleukin-6 receptor and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Contribution of the stalk sequence to the cleavage pattern of transmembrane proteins. Eur J Biochem 267:2624–2631 - PubMed
-
- Ayyadhury S, Heese K (2007) Neurotrophins—more than neurotrophic. Curr Immunol Rev 3:125–189
-
- Barker PA, Lomen-Hoerth C, Gensch EM, Meakin SO, Glass DJ, Shooter EM (1993) Tissue-specific alternative splicing generates two isoforms of the trkA receptor. J Biol Chem 268:15150–15157 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

