Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in tumor-bearing nude mice
- PMID: 20407895
- PMCID: PMC4332869
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-010-1323-z
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in tumor-bearing nude mice
Abstract
Purpose: AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) (AstraZeneca, Macclesfield, UK) is a novel small molecule MEK1/2 inhibitor that is currently being tested in Phase II trials. With the recent publication of human pharmacokinetic data from clinical studies, we now know the achievable levels and range of AZD6244 exposure in humans. This study aimed to describe the pharmacokinetic profile of AZD6244 in mice in order to design preclinical studies that recapitulate exposure levels in humans.
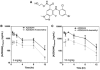
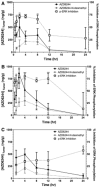
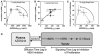
Methods: Male athymic, nude mice received subcutaneous inoculation of A375 human melanoma cells. Once tumors reached 400-700 mm(3), mice were given a single dose of either 5 or 10 mg/kg AZD6244 via oral gavage. Additionally, a subset of mice was dosed once daily for 1 week (10 mg/kg). Mice were killed and plasma and tissues were collected at various time points after the last dose. Samples were analyzed by LC/MS/MS for AZD6244 concentration. Additionally, pharmacodynamic endpoints such as tumor proliferation and ERK phosphorylation were analyzed at various time points after the last dose.
Results: After either a single dose or at steady state, at clinically equivalent exposures, AZD6244 effectively inhibits ERK phosphorylation and suppresses proliferation. Furthermore, we describe a hysteretic relationship between the pharmacokinetics and the pharmacodynamics of AZD6244 and both target and pharmacologic responses.
Conclusions: The information presented herein will drive the rational design of pre-clinical studies that are not only relevant to the clinical setting, but also pave the way to understand the biological response to AZD6244 treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
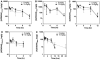



Similar articles
-
Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers.J Clin Oncol. 2008 May 1;26(13):2139-46. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4956. Epub 2008 Apr 7. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18390968 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical models.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Aug;6(8):2209-19. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0231. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17699718
-
The mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) induces growth arrest in melanoma cells and tumor regression when combined with docetaxel.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Jan 1;14(1):230-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1440. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18172275
-
Targeted inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase pathway with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Jan;6(1):138-46. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0436. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17237274
-
Selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142886) in the treatment of metastatic melanoma.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012 Apr;21(4):531-9. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2012.665871. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22394161 Review.
Cited by
-
Selumetinib Plus Docetaxel Compared With Docetaxel Alone and Progression-Free Survival in Patients With KRAS-Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The SELECT-1 Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2017 May 9;317(18):1844-1853. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.3438. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28492898 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase Ib Results of the Rational Combination of Selumetinib and Cyclosporin A in Advanced Solid Tumors with an Expansion Cohort in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 15;78(18):5398-5407. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0316. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30042150 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I dose-escalation study of selumetinib in combination with docetaxel or dacarbazine in patients with advanced solid tumors.BMC Cancer. 2017 Mar 6;17(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3143-6. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28264648 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of SMURF2 targeting on susceptibility to MEK inhibitors in melanoma.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013 Jan 2;105(1):33-46. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs471. Epub 2012 Dec 17. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013. PMID: 23250956 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of NFX-179 MEK inhibitor on cutaneous neurofibromas in persons with neurofibromatosis type 1.Sci Adv. 2024 May 3;10(18):eadk4946. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk4946. Epub 2024 May 1. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38691597 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Adjei AA, Cohen RB, Franklin W, Morris C, Wilson D, Molina JR, Hanson LJ, Gore L, Chow L, Leong S, Maloney L, Gordon G, Simmons H, Marlow A, Litwiler K, Brown S, Poch G, Kane K, Haney J, Eckhardt SG. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2139–2146. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ball DW, Jin N, Rosen DM, Dackiw A, Sidransky D, Xing M, Nelkin BD. Selective growth inhibition in BRAF mutant thyroid cancer by the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4712–4718. - PubMed
-
- Brose MS, Volpe P, Feldman M, Kumar M, Rishi I, Gerrero R, Einhorn E, Herlyn M, Minna J, Nicholson A, Roth JA, Albelda SM, Davies H, Cox C, Brignell G, Stephens P, Futreal PA, Wooster R, Stratton MR, Weber BL. BRAF and RAS mutations in human lung cancer and melanoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6997–7000. - PubMed
-
- Csajka C, Verotta D. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling: history and perspectives. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2006;33:227–279. - PubMed
-
- Danhof M, Visser SA. Pharmaco-electroencephalography and pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling in drug development: focus on preclinical steps. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2002;24(Suppl D):127–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

