Consequences of digital mammography in population-based breast cancer screening: initial changes and long-term impact on referral rates
- PMID: 20407901
- PMCID: PMC2914257
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-010-1786-7
Consequences of digital mammography in population-based breast cancer screening: initial changes and long-term impact on referral rates
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the referral pattern after the transition to full-field digital mammography (FFDM) in a population-based breast cancer screening programme.
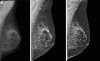
Methods: Preceding the nationwide digitalisation of the Dutch screening programme, an FFDM feasibility study was conducted. Detection and referral rates for FFDM and screen-film mammography (SFM) were compared for first and subsequent screens. Furthermore, radiological characteristics of referrals in digital screening were assessed.
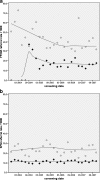
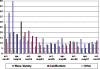
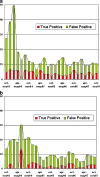
Results: A total of 312,414 screening mammograms were performed (43,913 digital and 268,501 conventional), with 4,473 consecutive referrals (966 following FFDM). Initially the FFDM referral rate peaked, and many false-positive results were noted as a consequence of pseudolesions and increased detection of (benign) microcalcifications. A higher overall referral rate was observed in FFDM screening in both first and subsequent examinations (p < .001), with a significant increase in cancer detection (p = .010).
Conclusion: As a result of initial inexperience with digital screening images implementing FFDM in a population-based breast cancer screening programme may lead to a strong, but temporary increase in referral. Dedicated training in digital screening for radiographers and screening radiologists is therefore recommended. Referral rates decrease and stabilise (learning curve effect) at a higher level than in conventional screening, yet with significantly enhanced cancer detection.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

