Changes in the levels of some acute-phase proteins in human immunodeficiency virus-1 infected patients, following interleukin-2 treatment
- PMID: 20408859
- PMCID: PMC2940158
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04145.x
Changes in the levels of some acute-phase proteins in human immunodeficiency virus-1 infected patients, following interleukin-2 treatment
Abstract
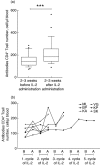
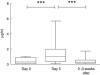
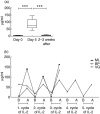
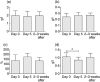
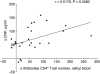
Intermittent interleukin (IL)-2 administration to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 infected patients is well documented and generally used, but there is limited information about the changes of acute-phase protein (APP) levels in response to this treatment. Fifteen patients undergoing highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART) treatment, with undetectable viral load, but low CD4+ cell count (<300/microl), have been treated with 3.6 M IU Proleukine administered twice daily by subcutaneous injection over 5 days. C-reactive protein (CRP), D-dimer, C3, C9, C1-inh and alpha-2HS glycoprotein levels were measured immediately before IL-2 administration, as well as on day 5 and 2-3 weeks thereafter. After IL-2 administration, both mean D-dimer and CRP levels increased significantly (P<0.001), but returned (P<0.001) to baseline within the subsequent 2-3 weeks. Alpha-2HS glycoprotein decreased immediately after IL-2 administration. No significant differences were detected in the levels of C3, C9 and C1-inh. A significant, positive correlation (r=0.5178, P=0.0008) was ascertained between the changes of CRP level, measured immediately before as well as 5 days after IL-2 administration, and changes in CD4 T cell counts measured 2-3 weeks before and after treatment, respectively. IL-2 administration induces rapid elevation of two major APPs (CRP, D-dimer). The positive correlation observed between the changes of CRP levels and CD4+ cell counts after IL-2 administration may indicate that the abrupt, but transitory overproduction of CRP might contribute to the CD4+ cell count-increasing effect of the drug and/ or may be associated with serious side effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-2 cycling causes transient increases in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and D-dimer that are not associated with plasma HIV-RNA levels.AIDS. 2009 Sep 24;23(15):2015-9. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832d72c6. AIDS. 2009. PMID: 19617815 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term clinical and surrogate marker effects of subcutaneous intermittent interleukin-2 without antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected patients.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008 Sep;62(3):583-6. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn238. Epub 2008 Jun 27. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18587135 Clinical Trial.
-
The virologic, immunologic, and clinical effects of interleukin 2 with potent antiretroviral therapy in patients with moderately advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection: a randomized controlled clinical trial--AIDS Clinical Trials Group 328.Arch Intern Med. 2007 Mar 26;167(6):597-605. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.6.597. Arch Intern Med. 2007. PMID: 17389292 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of interleukin-2 in patients with HIV infection.Drugs. 2010 Jun 18;70(9):1115-30. doi: 10.2165/10898620-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20518579 Review.
-
The potential role of interleukin-2 in HIV.AIDS. 2001 Feb;15 Suppl 2:S22-7. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200102002-00005. AIDS. 2001. PMID: 11424973 Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring acute phase proteins in retrovirus infected cats undergoing feline interferon-ω therapy.J Small Anim Pract. 2014 Jan;55(1):39-45. doi: 10.1111/jsap.12160. Epub 2013 Nov 27. J Small Anim Pract. 2014. PMID: 24279640 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term effects of intermittent IL-2 in HIV infection: extended follow-up of the INSIGHT STALWART Study.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047506. Epub 2012 Oct 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23082173 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Soluble mediators of inflammation in HIV and their implications for therapeutics and vaccine development.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012 Aug-Oct;23(4-5):193-206. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012. PMID: 22743035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Use of Recombinant Feline Interferon Omega Therapy as an Immune-Modulator in Cats Naturally Infected with Feline Immunodeficiency Virus: New Perspectives.Vet Sci. 2016 Oct 27;3(4):32. doi: 10.3390/vetsci3040032. Vet Sci. 2016. PMID: 29056740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith KA. Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications. Science. 1988;240:1169–76. - PubMed
-
- Vogler MA, Teppler H, Gelman R, et al. Daily low-dose subcutaneous interleukin-2 added to single- or dual-nucleoside therapy in HIV infection does not protect against CD4+ T-cell decline or improve other indices of immune function: results of a randomized controlled clinical trial (ACTG 248) J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2004;36:576–87. - PubMed
-
- Emery S, Abrams DI, Cooper DA, et al. The evaluation of subcutaneous proleukin (interleukin-2) in a randomized international trial: rationale, design, and methods of ESPRIT. Control Clin Trials. 2002;23:198–220. - PubMed
-
- Durier C, Capitant C, Lascaux AS, et al. Long-term effects of intermittent interleukin-2 therapy in chronic HIV-infected patients (ANRS 048-079 Trials) Aids. 2007;21:1887–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

