Interleukin-17 and its target genes: mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease
- PMID: 20409152
- PMCID: PMC2826676
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03240.x
Interleukin-17 and its target genes: mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease
Abstract
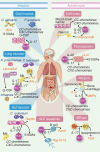
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) has emerged as a central player in the mammalian immune system. Although this cytokine exerts a host-defensive role in many infectious diseases, it promotes inflammatory pathology in autoimmunity and other settings. A myriad of studies have focused on how IL-17-producing cells are generated. However, the means by which IL-17 achieves its effects, either for the benefit or the detriment of the host, are due in large part to the induction of new gene expression. Whereas many IL-17 target genes are common to different disease states, in some cases the effects of IL-17 differ depending on the target cell, infectious site or pathogen. Gene products induced by IL-17 include cytokines (IL-6, granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor, tumour necrosis factor-alpha), chemokines (CXCL1, CXCL2, CCL20, among many others), inflammatory effectors (acute-phase protesins, complement) and antimicrobial proteins (defensins, mucins). Different cell types appear to respond differently to IL-17 in terms of target gene expression, with notable differences seen in mesenchymal and epithelial cells compared with cells of haematopoietic origin. Here, we summarize the major IL-17 target genes that mediate this cytokine's activities in both autoimmune and chronic diseases as well as during various types of infections.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources