The ubiquitin-proteasome system regulates plant hormone signaling
- PMID: 20409276
- PMCID: PMC3066055
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04112.x
The ubiquitin-proteasome system regulates plant hormone signaling
Abstract
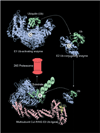
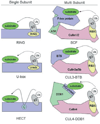
Plants utilize the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) to modulate nearly every aspect of growth and development. Ubiquitin is covalently attached to target proteins through the action of three enzymes known as E1, E2, and E3. The ultimate outcome of this post-translational modification depends on the nature of the ubiquitin linkage and the extent of polyubiquitination. In most cases, ubiquitination results in degradation of the target protein in the 26S proteasome. During the last 10 years it has become clear that the UPS plays a prominent regulatory role in hormone biology. E3 ubiquitin ligases in particular actively participate in hormone perception, de-repression of hormone signaling pathways, degradation of hormone specific transcription factors, and regulation of hormone biosynthesis. It is certain that additional functions will be discovered as more of the nearly 1200 potential E3s in plants are elucidated.
Figures

References
-
- Amador V, Monte E, Garcia-Martinez JL, Prat S. Gibberellins signal nuclear import of PHOR1, a photoperiod-responsive protein with homology to Drosophila armadillo. Cell. 2001;106:343–354. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt A, Lechner E, Hano P, et al. CUL4 associates with DDB1 and DET1 and its downregulation affects diverse aspects of development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2006;47:591–603. - PubMed
-
- Biswas KK, Oorua C, Higuchi K, et al. Genetic characterization of mutants resistant to the antiauxin p-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid reveals that AAR3, a gene encoding a DCN1 like protein, regulates reponses to the synthetic auxin 2′4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol. 2007;145:773–785. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Browse J. Jasmonate: an oxylipin signal with many roles in plants. Vitam. Horm. 2005;72:431–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

