Epigenetic chromatin modifiers in barley: IV. The study of barley polycomb group (PcG) genes during seed development and in response to external ABA
- PMID: 20409301
- PMCID: PMC3095347
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-73
Epigenetic chromatin modifiers in barley: IV. The study of barley polycomb group (PcG) genes during seed development and in response to external ABA
Abstract
Background: Epigenetic phenomena have been associated with the regulation of active and silent chromatin states achieved by modifications of chromatin structure through DNA methylation, and histone post-translational modifications. The latter is accomplished, in part, through the action of PcG (Polycomb group) protein complexes which methylate nucleosomal histone tails at specific sites, ultimately leading to chromatin compaction and gene silencing. Different PcG complex variants operating during different developmental stages have been described in plants. In particular, the so-called FIE/MEA/FIS2 complex governs the expression of genes important in embryo and endosperm development in Arabidopsis. In our effort to understand the epigenetic mechanisms regulating seed development in barley (Hordeum vulgare), an agronomically important monocot plant cultivated for its endosperm, we set out to characterize the genes encoding barley PcG proteins.
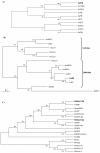
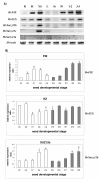
Results: Four barley PcG gene homologues, named HvFIE, HvE(Z), HvSu(z)12a, and HvSu(z)12b were identified and structurally and phylogenetically characterized. The corresponding genes HvFIE, HvE(Z), HvSu(z)12a, and HvSu(z)12b were mapped onto barley chromosomes 7H, 4H, 2H and 5H, respectively. Expression analysis of the PcG genes revealed significant differences in gene expression among tissues and seed developmental stages and between barley cultivars with varying seed size. Furthermore, HvFIE and HvE(Z) gene expression was responsive to the abiotic stress-related hormone abscisic acid (ABA) known to be involved in seed maturation, dormancy and germination.
Conclusion: This study reports the first characterization of the PcG homologues, HvFIE, HvE(Z), HvSu(z)12a and HvSu(z)12b in barley. All genes co-localized with known chromosomal regions responsible for malting quality related traits, suggesting that they might be used for developing molecular markers to be applied in marker assisted selection. The PcG differential expression pattern in different tissues and seed developmental stages as well as in two barley cultivars with different seed size is suggestive of a role for these genes in barley seed development. HvFIE and HvE(Z) were also found to be induced by the plant hormone ABA implying an association with ABA-mediated processes during seed development, germination and stress response.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

