Papillary thyroid cancer associated with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis: a case report
- PMID: 20409321
- PMCID: PMC2873447
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-4-110
Papillary thyroid cancer associated with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis is the most common cause of euvolemic hypo-osmolality. This syndrome is associated with a wide variety of diseases. However, its most frequent causes are related to malignancies, especially lung cancer. In this case report, we describe an unknown association of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis with papillary thyroid cancer.
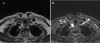
Case presentation: We present the case of a 71-year-old Caucasian, German woman with marked hyponatremia and neurological symptoms. After a detailed clinical investigation, the common causes of syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis and other malignancies were ruled out. A thyroid nodule was detected by ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Although fine needle aspiration cytology showed negative results, our patient underwent surgery. Papillary thyroid cancer was later diagnosed. After total thyroidectomy, a complete remission of the clinical symptoms occurred and our patient subsequently had iodine-131 radioactive therapy. Hyponatremia was no longer observed during the follow-up investigations.
Conclusion: This is the first reported case of paraneoplastic syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis caused by papillary thyroid carcinoma. Since its symptoms occurred before the development of local symptoms, total thyroidectomy may provide a timely and efficient treatment for the underlying malignancy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis.Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Jul;1(4):537-547. doi: 10.1586/17446651.1.4.537. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 30290457
-
Autonomously functioning thyroid nodule treated with radioactive iodine and later diagnosed as papillary thyroid cancer.Hormones (Athens). 2008 Apr-Jun;7(2):175-9. doi: 10.1007/BF03401510. Hormones (Athens). 2008. PMID: 18477556
-
Management of thyroid cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines.J Laryngol Otol. 2016 May;130(S2):S150-S160. doi: 10.1017/S0022215116000578. J Laryngol Otol. 2016. PMID: 27841128 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer metastases to the thyroid gland - an uncommon sentinel for diffuse metastatic disease: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2017 Sep 22;11(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s13256-017-1441-x. J Med Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28934992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Papillary thyroid carcinoma in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.Thyroid. 2011 Nov;21(11):1273-7. doi: 10.1089/thy.2011.0063. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Thyroid. 2011. PMID: 21877933 Review.
Cited by
-
Cold Agglutinin Disease: A Rare Paraneoplastic Manifestation of a Thyroid Malignancy.Cureus. 2024 Aug 27;16(8):e67924. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67924. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39328603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amatruda TT Jr, Mulrow PJ, Gallagher JC, Sawyer WH. Carcinoma of the lung with inappropriate antidiuresis: demonstration of antidiuretic hormone-like activity in tumor extract. N Engl J Med. 1963;269:544–549. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

