Major role for mRNA stability in shaping the kinetics of gene induction
- PMID: 20409322
- PMCID: PMC2864252
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-259
Major role for mRNA stability in shaping the kinetics of gene induction
Abstract
Background: mRNA levels in cells are determined by the relative rates of RNA production and degradation. Yet, to date, most analyses of gene expression profiles were focused on mechanisms which regulate transcription, while the role of mRNA stability in modulating transcriptional networks was to a large extent overlooked. In particular, kinetic waves in transcriptional responses are usually interpreted as resulting from sequential activation of transcription factors.
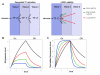
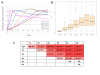
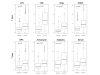
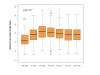
Results: In this study, we examined on a global scale the role of mRNA stability in shaping the kinetics of gene response. Analyzing numerous expression datasets we revealed a striking global anti-correlation between rapidity of induction and mRNA stability, fitting the prediction of a kinetic mathematical model. In contrast, the relationship between kinetics and stability was less significant when gene suppression was analyzed. Frequently, mRNAs that are stable under standard conditions were very rapidly down-regulated following stimulation. Such effect cannot be explained even by a complete shut-off of transcription, and therefore indicates intense modulation of RNA stability.
Conclusion: Taken together, our results demonstrate the key role of mRNA stability in determining induction kinetics in mammalian transcriptional networks.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

