Production of recombinant cholesterol oxidase containing covalently bound FAD in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20409334
- PMCID: PMC2890692
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-10-33
Production of recombinant cholesterol oxidase containing covalently bound FAD in Escherichia coli
Abstract
Background: Cholesterol oxidase is an alcohol dehydrogenase/oxidase flavoprotein that catalyzes the dehydrogenation of C(3)-OH of cholesterol. It has two major biotechnological applications, i.e. in the determination of serum (and food) cholesterol levels and as biocatalyst providing valuable intermediates for industrial steroid drug production. Cholesterol oxidases of type I are those containing the FAD cofactor tightly but not covalently bound to the protein moiety, whereas type II members contain covalently bound FAD. This is the first report on the over-expression in Escherichia coli of type II cholesterol oxidase from Brevibacterium sterolicum (BCO).
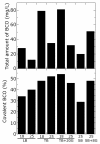
Results: Design of the plasmid construct encoding the mature BCO, optimization of medium composition and identification of the best cultivation/induction conditions for growing and expressing the active protein in recombinant E. coli cells, concurred to achieve a valuable improvement: BCO volumetric productivity was increased from approximately 500 up to approximately 25000 U/L and its crude extract specific activity from 0.5 up to 7.0 U/mg protein. Interestingly, under optimal expression conditions, nearly 55% of the soluble recombinant BCO is produced as covalently FAD bound form, whereas the protein containing non-covalently bound FAD is preferentially accumulated in insoluble inclusion bodies.
Conclusions: Comparison of our results with those published on non-covalent (type I) COs expressed in recombinant form (either in E. coli or Streptomyces spp.), shows that the fully active type II BCO can be produced in E. coli at valuable expression levels. The improved over-production of the FAD-bound cholesterol oxidase will support its development as a novel biotool to be exploited in biotechnological applications.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

