A combination of multisite phosphorylation and substrate sequestration produces switchlike responses
- PMID: 20409458
- PMCID: PMC2856190
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.12.4307
A combination of multisite phosphorylation and substrate sequestration produces switchlike responses
Abstract
The phosphorylation of a protein on multiple sites has been proposed to promote the switchlike regulation of protein activity. Recent theoretical work, however, indicates that multisite phosphorylation, by itself, is less effective at creating switchlike responses than had been previously thought. The phosphorylation of a protein often alters its spatial localization, or its association with other proteins, and this sequestration can alter the accessibility of the substrate to the relevant kinases and phosphatases. Sequestration thus has the potential to interact with multisite phosphorylation to modulate ultrasensitivity and threshold. Here, using simple ordinary differential equations to represent phosphorylation, dephosphorylation, and binding/sequestration, we demonstrate that the combination of multisite phosphorylation and regulated substrate sequestration can produce a response that is both a good threshold and a good switch. Several strategies are explored, including both stronger and weaker sequestration with successive phosphorylations, as well as combinations that are more elaborate. In some strategies, such as when phosphorylation and dephosphorylation are segregated, a near-optimal switch is possible, where the effective Hill number equals the number of phosphorylation sites.
Copyright 2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


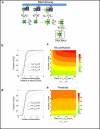


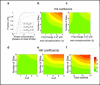
References
-
- Manning G., Whyte D.B., Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298:1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Mann M., Ong S.E., Pandey A. Analysis of protein phosphorylation using mass spectrometry: deciphering the phosphoproteome. Trends Biotechnol. 2002;20:261–268. - PubMed
-
- Barford D., Hu S.H., Johnson L.N. Structural mechanism for glycogen phosphorylase control by phosphorylation and AMP. J. Mol. Biol. 1991;218:233–260. - PubMed
-
- Shacter-Noiman E., Chock P.B., Stadtman E.R. Protein phosphorylation as a regulatory device. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B. 1983;302:157–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

