Agonists and antagonists bind to an A-A interface in the heteromeric 5-HT3AB receptor
- PMID: 20409468
- PMCID: PMC2856171
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.12.4313
Agonists and antagonists bind to an A-A interface in the heteromeric 5-HT3AB receptor
Abstract
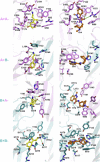
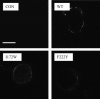
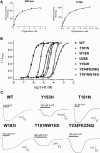
The 5-HT3 receptor is a member of the Cys-loop family of transmitter receptors. It can function as a homopentamer (5-HT3A-only subunits) or as a heteropentamer. The 5-HT3AB receptor is the best characterized heteropentamer. This receptor differs from a homopentamer in its kinetics, voltage dependence, and single-channel conductance, but its pharmacology is similar. To understand the contribution of the 5-HT3B subunit to the binding site, we created homology models of 5-HT3AB receptors and docked 5-HT and granisetron into AB, BA, and BB interfaces. To test whether ligands bind in any or all of these interfaces, we mutated amino acids that are important for agonist and antagonist binding in the 5-HT3A subunit to their corresponding residues in the 5-HT3B subunit and vice versa. Changes in [3H]granisetron binding affinity (Kd) and 5-HT EC50 were determined using receptors expressed in HEK-293 cells and Xenopus oocytes, respectively. For all A-to-B mutant receptors, except T181N, antagonist binding was altered or eliminated. Functional studies revealed that either the receptors were nonfunctional or the EC50 values were increased. In B-to-A mutant receptors there were no changes in Kd, although EC50 values and Hill slopes, except for N170T mutant receptors, were similar to those for 5-HT3A receptors. Thus, the experimental data do not support a contribution of the 5-HT3B subunit to the binding pocket, and we conclude that both 5-HT and granisetron bind to an AA binding site in the heteromeric 5-HT3AB receptor.
Copyright 2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A single channel mutation alters agonist efficacy at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;170(2):391-402. doi: 10.1111/bph.12287. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23822584 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of recognition loops B and D in the activation of human 5-HT₃ receptors by 5-HT and meta-chlorophenylbiguanide.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Oct;73:398-403. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.017. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23810831
-
Allosteric activation of the 5-HT3AB receptor by mCPBG.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Apr;91:103-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.12.018. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25541413 Free PMC article.
-
Discriminating between 5-HT₃A and 5-HT₃AB receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Jun;169(4):736-47. doi: 10.1111/bph.12166. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23489111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 (5-HT3) receptor reveals a novel determinant of single-channel conductance.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Jun;32(Pt3):547-52. doi: 10.1042/BST0320547. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15157181 Review.
Cited by
-
A single channel mutation alters agonist efficacy at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;170(2):391-402. doi: 10.1111/bph.12287. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23822584 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mechanism of modulation at a ligand-gated ion channel; action of 5-Cl-indole at the 5-HT3 A receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;173(24):3467-3479. doi: 10.1111/bph.13638. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27677804 Free PMC article.
-
The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2013/14: ligand-gated ion channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;170(8):1582-606. doi: 10.1111/bph.12446. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24528238 Free PMC article.
-
VUF10166, a novel compound with differing activities at 5-HT₃A and 5-HT₃AB receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 May;341(2):350-9. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.190769. Epub 2012 Feb 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22306960 Free PMC article.
-
Agonists and antagonists induce different palonosetron dissociation rates in 5-HT₃A and 5-HT₃AB receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Oct;73:241-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23747573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reeves D.C., Lummis S.C.R. The molecular basis of the structure and function of the 5-HT3 receptor: a model ligand-gated ion channel (review) Mol. Membr. Biol. 2002;19:11–26. - PubMed
-
- Davies P.A., Pistis M., Kirkness E.F. The 5-HT3B subunit is a major determinant of serotonin-receptor function. Nature. 1999;397:359–363. - PubMed
-
- Niesler B., Frank B., Rappold G.A. Cloning, physical mapping and expression analysis of the human 5-HT3 serotonin receptor-like genes HTR3C, HTR3D and HTR3E. Gene. 2003;310:101–111. - PubMed
-
- Hanna M.C., Davies P.A., Kirkness E.F. Evidence for expression of heteromeric serotonin 5-HT3 receptors in rodents. J. Neurochem. 2000;75:240–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

