Role of the transmembrane potential in the membrane proton leak
- PMID: 20409469
- PMCID: PMC2856137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.12.4301
Role of the transmembrane potential in the membrane proton leak
Abstract
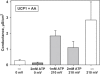
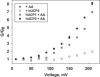
The molecular mechanism responsible for the regulation of the mitochondrial membrane proton conductance (G) is not clearly understood. This study investigates the role of the transmembrane potential (DeltaPsim) using planar membranes, reconstituted with purified uncoupling proteins (UCP1 and UCP2) and/or unsaturated FA. We show that high DeltaPsim (similar to DeltaPsim in mitochondrial State IV) significantly activates the protonophoric function of UCPs in the presence of FA. The proton conductance increases nonlinearly with DeltaPsim. The application of DeltaPsim up to 220 mV leads to the overriding of the protein inhibition at a constant ATP concentration. Both, the exposure of FA-containing bilayers to high DeltaPsim and the increase of FA membrane concentration bring about the significant exponential Gm increase, implying the contribution of FA in proton leak. Quantitative analysis of the energy barrier for the transport of FA anions in the presence and absence of protein suggests that FA- remain exposed to membrane lipids while crossing the UCP-containing membrane. We believe this study shows that UCPs and FA decrease DeltaPsim more effectively if it is sufficiently high. Thus, the tight regulation of proton conductance and/or FA concentration by DeltaPsim may be key in mitochondrial respiration and metabolism.
Copyright 2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
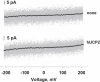
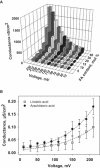
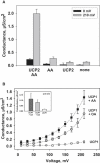
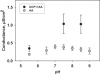
References
-
- Nicholls D.G. A history of UCP1. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2001;29:751–755. - PubMed
-
- Nedergaard J., Golozoubova V., Cannon B. UCP1: the only protein able to mediate adaptive non-shivering thermogenesis and metabolic inefficiency. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2001;1504:82–106. - PubMed
-
- Skulachev V.P. Uncoupling: new approaches to an old problem of bioenergetics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998;1363:100–124. - PubMed
-
- Dlasková A., Hlavatá L., Jezek P. Oxidative stress caused by blocking of mitochondrial complex I H(+) pumping as a link in aging/disease vicious cycle. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008;40:1792–1805. - PubMed
-
- Brand M.D., Affourtit C., Parker N. Mitochondrial superoxide: production, biological effects, and activation of uncoupling proteins. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004;37:755–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

