Assembly pathway of a designed alpha-helical protein fiber
- PMID: 20409488
- PMCID: PMC2856164
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.12.4309
Assembly pathway of a designed alpha-helical protein fiber
Abstract
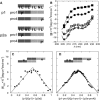
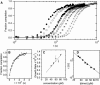
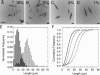
Interest in the design of peptide-based fibrous materials is growing because it opens possibilities to explore fundamental aspects of peptide self-assembly and to exploit the resulting structures--for example, as scaffolds for tissue engineering. Here we investigate the assembly pathway of self-assembling fibers, a rationally designed alpha-helical coiled-coil system comprising two peptides that assemble on mixing. The dimensions spanned by the peptides and final structures (nanometers to micrometers), and the timescale over which folding and assembly occur (seconds to hours), necessitate a multi-technique approach employing spectroscopy, analytical ultracentrifugation, electron and light microscopy, and protein design to produce a physical model. We show that fibers form via a nucleation and growth mechanism. The two peptides combine rapidly (in less than seconds) to form sticky ended, partly helical heterodimers. A lag phase follows, on the order of tens of minutes, and is concentration-dependent. The critical nucleus comprises six to eight partially folded dimers. Growth is then linear in dimers, and subsequent fiber growth occurs in hours through both elongation and thickening. At later times (several hours), fibers grow predominantly through elongation. This kinetic, biomolecular description of the folding-and-assembly process allows the self-assembling fiber system to be manipulated and controlled, which we demonstrate through seeding experiments to obtain different distributions of fiber lengths. This study and the resulting mechanism we propose provide a potential route to achieving temporal control of functional fibers with future applications in biotechnology and nanoscale science and technology.
Copyright 2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
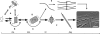


References
-
- Woolfson D.N. The design of coiled-coil structures and assemblies. Adv. Protein Chem. 2005;70:79–112. - PubMed
-
- Yeates T.O., Padilla J.E. Designing supramolecular protein assemblies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2002;12:464–470. - PubMed
-
- MacPhee C.E., Woolfson D.N. Engineered and designed peptide-based fibrous biomaterials. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mat. Sci. 2004;8:141–149.
-
- Fairman R., Akerfeldt K.S. Peptides as novel smart materials. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005;15:453–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

