Treating hypertension while protecting the vulnerable islet in the cardiometabolic syndrome
- PMID: 20409906
- PMCID: PMC2867460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jash.2007.12.002
Treating hypertension while protecting the vulnerable islet in the cardiometabolic syndrome
Abstract
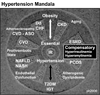
Hypertension, a multifactorial-polygenic disease, interacts with multiple environmental stressors and results in functional and structural changes in numerous end organs, including the cardiovascular system. This can result in coronary heart disease, stroke, peripheral vascular disease, congestive heart failure, end-stage renal disease, insulin resistance, and damage to the pancreatic islet. Hypertension is the most important modifiable risk factor for major health problems encountered in clinical practice. Whereas hypertension was once thought to be a medical condition based on discrete blood pressure readings, a new concept has emerged defining hypertension as part of a complex and progressive metabolic and cardiovascular disease, an important part of a cardiometabolic syndrome. The central role of insulin resistance, oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, metabolic signaling defects within tissues, and the role of enhanced tissue renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activity as it relates to hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus are emphasized. Additionally, this review focuses on the effect of hypertension on functional and structural changes associated with the vulnerable pancreatic islet. Various classes of antihypertensive drugs are reviewed, especially their roles in delaying or preventing damage to the vulnerable pancreatic islet, and thus delaying the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures






References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL, Jr, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- Klag MJ, Whelton PK, Randall BL, Neaton JD, Brancati FL, Ford CE, et al. Blood pressure and end-stage renal disease in men. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:13–18. - PubMed
-
- Stamler J, Vaccaro O, Neaton JD, Wentworth D. Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:434–444. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MR, Sowers JR. Hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Insulin. 2006;1:22–37.
-
- Sowers JR. Insulin resistance and hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286:H1597–H1602. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

