APOE genotype is associated with oral herpetic lesions but not genital or oral herpes simplex virus shedding
- PMID: 20410080
- PMCID: PMC2881187
- DOI: 10.1136/sti.2009.039735
APOE genotype is associated with oral herpetic lesions but not genital or oral herpes simplex virus shedding
Abstract
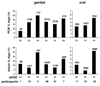
Background: Apolipoprotein E is polymorphic in the human population. APOE4 has previously been reported to correlate with symptomatic oral and genital herpes disease.
Methods: APOE was genotyped in 182 subjects with herpes simplex virus (HSV) 2 and in 62 subjects with HSV-1, including 44 subjects with both viral types for a total of 200 adults. HSV shedding was measured by PCR from swab samples obtained daily from mucosa for at least 30 days. Participants also maintained a diary of oral or genital lesions.
Results: The APOE genotypes observed reflected the US white population and the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Genital and oral HSV shedding was detected on 17.2% and 3.7% of overall days, respectively, whereas genital and oral lesion rates were 10.1% and 2.9%. Using Poisson regression and adjusting for known correlates of HSV shedding, a significant association was not observed between the APOE genotype and genital or oral HSV shedding, or genital HSV lesions. However, the presence of the APOE4 allele was associated with a higher rate of oral herpetic lesions, with a relative risk of 4.64 (95% CI 1.32 to 15.05, p=0.016).
Conclusions: Variation at the APOE locus may be associated with clinical manifestations of HSV-1 infection, but does not appear to correlate with herpes simplex viral reactivation in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reactivation of genital herpes simplex virus type 2 infection in asymptomatic seropositive persons.N Engl J Med. 2000 Mar 23;342(12):844-50. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200003233421203. N Engl J Med. 2000. PMID: 10727588
-
The effect of daily valacyclovir suppression on herpes simplex virus type 2 viral shedding in HSV-2 seropositive subjects without a history of genital herpes.Sex Transm Dis. 2008 Mar;35(3):286-90. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31815b0132. Sex Transm Dis. 2008. PMID: 18157071 Clinical Trial.
-
Genital Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Shedding Among Adults With and Without HIV Infection in Uganda.J Infect Dis. 2016 Feb 1;213(3):439-47. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv451. Epub 2015 Oct 20. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26486633 Free PMC article.
-
Oral shedding of herpes simplex virus type 1: a review.J Oral Pathol Med. 1997 Nov;26(10):441-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1997.tb00012.x. J Oral Pathol Med. 1997. PMID: 9416573 Review.
-
HSV shedding.Antiviral Res. 2004 Aug;63 Suppl 1:S19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2004.06.004. Antiviral Res. 2004. PMID: 15450382 Review.
Cited by
-
Herpes simplex virus, early neuroimaging markers and incidence of Alzheimer's disease.Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 31;11(1):414. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01532-2. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34333531 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of apolipoprotein E facilitates Herpes simplex virus 1 attachment and release.Npj Viruses. 2025 Feb 22;3(1):13. doi: 10.1038/s44298-025-00099-9. Npj Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40295730 Free PMC article.
-
HSV-1 clinical isolates with unique in vivo and in vitro phenotypes and insight into genomic differences.J Neurovirol. 2017 Apr;23(2):171-185. doi: 10.1007/s13365-016-0485-9. Epub 2016 Oct 13. J Neurovirol. 2017. PMID: 27739035
-
HLA Class I and II alleles, heterozygosity and HLA-KIR interactions are associated with rates of genital HSV shedding and lesions.Genes Immun. 2016 Dec;17(7):412-418. doi: 10.1038/gene.2016.42. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Genes Immun. 2016. PMID: 27853144 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Labialis, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Helicobacter pylori, and Cytomegalovirus Infections and Risk of Dementia: The Framingham Heart Study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;82(2):593-605. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200957. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 34057145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu F, Sternberg MR, Kottiri BJ, McQuillan GM, Lee FK, Nahmias AJ, et al. Trends in herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 seroprevalence in the United States. JAMA. 2006;296(8):964–973. - PubMed
-
- Wald A, Zeh J, Selke S, Warren T, Ryncarz AJ, Ashley R, et al. Reactivation of genital herpes simplex virus type 2 infection in asymptomatic seropositive persons. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(12):844–850. - PubMed
-
- Corey L. Herpes simplex viruses. In: Kasper DL, Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, editors. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company; 2004. pp. 1035–1042.
-
- Itzhaki RF, Lin WR, Shang D, Wilcock GK, Faragher B, Jamieson GA. Herpes simplex virus type 1 in brain and risk of Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1997;349(9047):241–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
