GSK3 beta regulates myelin-dependent axon outgrowth inhibition through CRMP4
- PMID: 20410116
- PMCID: PMC6632347
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6154-09.2010
GSK3 beta regulates myelin-dependent axon outgrowth inhibition through CRMP4
Abstract
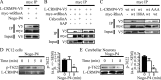
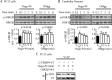
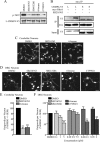
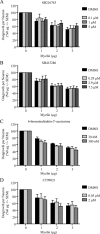
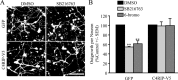
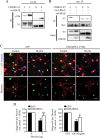
Myelin-associated inhibitors (MAIs) contribute to failed regeneration in the CNS. The intracellular signaling pathways through which MAIs block axonal repair remain largely unknown. Here, we report that the kinase GSK3beta is directly phosphorylated and inactivated by MAIs, consequently regulating protein-protein interactions that are critical for myelin-dependent inhibition. Inhibition of GSK3beta mimics the neurite outgrowth inhibitory effect of myelin. The inhibitory effects of GSK3beta inhibitors and myelin are not additive indicating that GSK3beta is a major effector of MAIs. Consistent with this, overexpression of GSK3beta attenuates myelin inhibition. MAI-dependent phosphorylation and inactivation of GSK3beta regulate phosphorylation of CRMP4, a cytosolic regulator of myelin inhibition, and its ability to complex with RhoA. Introduction of a CRMP4 antagonist attenuates the neurite outgrowth inhibitory properties of GSK3beta inhibitors. We describe the first example of GSK3beta inactivation in response to inhibitory ligands and link the neurite outgrowth inhibitory effects of GSK3beta inhibition directly to CRMP4. These findings raise the possibility that GSK3beta inhibition will not effectively promote long-distance CNS regeneration following trauma such as spinal cord injury.
Figures

References
-
- Alabed YZ, Grados-Munro E, Ferraro GB, Hsieh SH, Fournier AE. Neuronal responses to myelin are mediated by ROCK. J Neurochem. 2006;96:1616–1625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
