Target-dependent regulation of neurotransmitter specification and embryonic neuronal calcium spike activity
- PMID: 20410131
- PMCID: PMC2871059
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5659-09.2010
Target-dependent regulation of neurotransmitter specification and embryonic neuronal calcium spike activity
Abstract
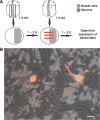
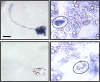
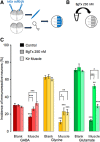
Neurotransmitter specification has been shown to depend on genetic programs and electrical activity; however, target-dependent regulation also plays important roles in neuronal development. We have investigated the impact of muscle targets on transmitter specification in Xenopus spinal neurons using a neuron-muscle coculture system. We find that neuron-muscle contact reduces the number of neurons expressing the noncholinergic transmitters GABA, glycine, and glutamate, while having no effect on the incidence of ChAT expression. We show that muscle activity is necessary for target-dependent reduction of noncholinergic transmitter expression. In addition, we demonstrate that coculture with muscle cells suppresses early spontaneous calcium spike activity in neurons and the presence of muscle cells abolishes activity-dependent transmitter specification. The results indicate that target-dependent regulation can be crucial in establishing neurotransmitter phenotypes and altering early neuronal excitability.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Activity-dependent homeostatic specification of transmitter expression in embryonic neurons.Nature. 2004 Jun 3;429(6991):523-30. doi: 10.1038/nature02518. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15175743
-
The role of voltage-gated calcium channels in neurotransmitter phenotype specification: Coexpression and functional analysis in Xenopus laevis.J Comp Neurol. 2014 Aug 1;522(11):2518-31. doi: 10.1002/cne.23547. Epub 2014 Apr 12. J Comp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24477801 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent neurotransmitter-receptor matching at the neuromuscular junction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 2;104(1):335-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607450104. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17190810 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestrating neuronal differentiation: patterns of Ca2+ spikes specify transmitter choice.Trends Neurosci. 2004 Jul;27(7):415-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2004.05.003. Trends Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15219741 Review.
-
Homeostatic activity-dependent paradigm for neurotransmitter specification.Cell Calcium. 2005 May;37(5):417-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2005.01.021. Cell Calcium. 2005. PMID: 15820389 Review.
Cited by
-
From induction to conduction: how intrinsic transcriptional priming of extrinsic neuronal connectivity shapes neuronal identity.Open Biol. 2014 Oct;4(10):140144. doi: 10.1098/rsob.140144. Open Biol. 2014. PMID: 25297387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium Activity Dynamics Correlate with Neuronal Phenotype at a Single Cell Level and in a Threshold-Dependent Manner.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 16;20(8):1880. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081880. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30995769 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous activity regulates Robo1 transcription to mediate a switch in thalamocortical axon growth.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Jul 8;15(8):1134-43. doi: 10.1038/nn.3160. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22772332
-
Glycine Receptor Inhibition Differentially Affect Selected Neuronal Populations of the Developing Embryonic Cortex, as Evidenced by the Analysis of Spontaneous Calcium Oscillations.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 28;21(21):8013. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218013. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33126495 Free PMC article.
-
Dissection, culture, and analysis of Xenopus laevis embryonic retinal tissue.J Vis Exp. 2012 Dec 23;(70):4377. doi: 10.3791/4377. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 23287809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnett J, Baecker P, Routledge-Ward C, Bursztyn-Pettegrew H, Chow J, Nguyen B, Bach C, Chan H, Tuszynski MH, Yoshida K. Human beta nerve growth factor obtained from a baculovirus expression system has potent in vitro and in vivo neurotrophic activity. Exp Neurol. 1990;110:11–24. - PubMed
-
- Borodinsky LA, Root CM, Cronin JA, Sann SB, Gu X, Spitzer NC. Activity-dependent homeostatic specification of transmitter expression in embryonic neurons. Nature. 2004;420:523–530. - PubMed
-
- Brosenitsch TA, Katz DM. Expression of Phox2 transcription factors and induction of the dopaminergic phenotype in primary sensory neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002;20:447–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
