A functional dynamic scoring model to elucidate the significance of post-induction interim fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography findings in patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma
- PMID: 20410186
- PMCID: PMC2895046
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.016105
A functional dynamic scoring model to elucidate the significance of post-induction interim fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography findings in patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma
Abstract
Background: The findings of interim fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET/CT) predict progression-free survival of patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma. Historically, the assessment was based on a static all-or-none scoring system. However, the clinical significance of any positivity in interim FDG-PET/CT has not been defined.
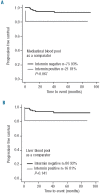
Design and methods: Ninety-six patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma who underwent interim FDG-PET/CT were evaluated using dynamic and visual scores, employing mediastinal or liver blood pool uptake as a comparator. FDG-PET/CT was prospectively defined as positive if any abnormal F(18)FDG uptake was present. In a retrospective analysis dynamic score 0 indicated resolution of all disease sites; score 1 defined a single residual focus; score 2 denoted a reduction in the number of foci; score 3 defined a reduction in intensity with no reduction in number; and score 4 indicated no change in the number and intensity of foci or appearance of new foci.
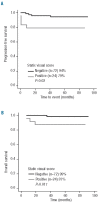
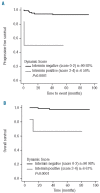
Results: The dynamic visual score review reduced the number of positive interim studies from 24 to 6 if a score of 2 or less was considered negative, with significantly better specificity (96%) as compared to static visual scores (78%-86%). The 5-year progression-free survival and overall survival rates in patients who had a negative dynamic score were 92% and 97%, respectively; the corresponding figures for patients with positive results were 50% and 67%.
Conclusions: A dynamic visual score may be a better indicator for tailoring therapy than static visual scoring.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Whole-body positron emission tomography using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose for posttreatment evaluation in Hodgkin's disease and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma has higher diagnostic and prognostic value than classical computed tomography scan imaging.Blood. 1999 Jul 15;94(2):429-33. Blood. 1999. PMID: 10397709
-
CT-based texture analysis potentially provides prognostic information complementary to interim fdg-pet for patients with hodgkin's and aggressive non-hodgkin's lymphomas.Eur Radiol. 2017 Mar;27(3):1012-1020. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4470-8. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Eur Radiol. 2017. PMID: 27380902 Free PMC article.
-
Progression-free survival of early interim PET-positive patients with advanced stage Hodgkin's lymphoma treated with BEACOPPescalated alone or in combination with rituximab (HD18): an open-label, international, randomised phase 3 study by the German Hodgkin Study Group.Lancet Oncol. 2017 Apr;18(4):454-463. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30103-1. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28236583 Clinical Trial.
-
The role of 18F-FDG PET and 18F-FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of pediatric Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.Hell J Nucl Med. 2013 Sep-Dec;16(3):230-6. doi: 10.1967/s0024499100091. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Hell J Nucl Med. 2013. PMID: 24137577 Review.
-
Predictive value of interim positron emission tomography in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Jan;46(1):65-79. doi: 10.1007/s00259-018-4103-3. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30141066 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interim PET-results for prognosis in adults with Hodgkin lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prognostic factor studies.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 16;9(9):CD012643. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012643.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 13;1:CD012643. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012643.pub3. PMID: 31525824 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Plasma thymus and activation-regulated chemokine as an early response marker in classical Hodgkin's lymphoma.Haematologica. 2012 Mar;97(3):410-5. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.053199. Epub 2011 Nov 4. Haematologica. 2012. PMID: 22058214 Free PMC article.
-
PET/CT adapted therapy in Hodgkin disease: current state of the art and future directions.Curr Oncol Rep. 2012 Oct;14(5):403-10. doi: 10.1007/s11912-012-0250-z. Curr Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22700011 Review.
-
Positron emission tomography scanning: a new paradigm for the management of Hodgkin's lymphoma.Haematologica. 2010 Jul;95(7):1046-8. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.024885. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 20595100 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
A semi-automatic technique to quantify complex tuberculous lung lesions on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computerised tomography images.EJNMMI Res. 2018 Jun 25;8(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s13550-018-0411-7. EJNMMI Res. 2018. PMID: 29943161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gallamini A, Hutchings M, Rigacci L, Specht L, Merli F, Hansen M, et al. Early interim 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography is prognostically superior to international prognostic score in advanced-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a report from a joint Italian-Danish study. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(24):3746–52. - PubMed
-
- Kirby AM, Mikhaeel NG. The role of FDG PET in the management of lymphoma: what is the evidence base? Nucl Med Commun. 2007;28(5):335–54. - PubMed
-
- Hutchings M, Mikhaeel NG, Fields PA, Nunan T, Timothy AR. Prognostic value of interim FDG-PET after two or three cycles of chemotherapy in Hodgkin lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2005;16(7):1160–8. - PubMed
-
- Hutchings M, Loft A, Hansen M, Pedersen LM, Buhl T, Jurlander J, et al. FDG-PET after two cycles of chemotherapy predicts treatment failure and progression-free survival in Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2006;107(1):52–9. - PubMed
-
- Terasawa T, Lau J, Bardet S, Couturier O, Hotta T, Hutchings M, et al. Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for interim response assessment of advanced-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a systematic review. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(11):1906–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

