Lentiviral overexpression of GRK6 alleviates L-dopa-induced dyskinesia in experimental Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 20410529
- PMCID: PMC2933751
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000664
Lentiviral overexpression of GRK6 alleviates L-dopa-induced dyskinesia in experimental Parkinson's disease
Abstract
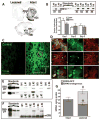
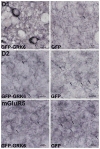
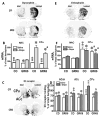
Parkinson's disease is caused primarily by degeneration of brain dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the consequent deficit of dopamine in the striatum. Dopamine replacement therapy with the dopamine precursor l-dopa is the mainstay of current treatment. After several years, however, the patients develop l-dopa-induced dyskinesia, or abnormal involuntary movements, thought to be due to excessive signaling via dopamine receptors. G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) control desensitization of dopamine receptors. We found that dyskinesia is attenuated by lentivirus-mediated overexpression of GRK6 in the striatum in rodent and primate models of Parkinson's disease. Conversely, reduction of GRK6 concentration by microRNA delivered with lentiviral vector exacerbated dyskinesia in parkinsonian rats. GRK6 suppressed dyskinesia in monkeys without compromising the antiparkinsonian effects of l-dopa and even prolonged the antiparkinsonian effect of a lower dose of l-dopa. Our finding that increased availability of GRK6 ameliorates dyskinesia and increases duration of the antiparkinsonian action of l-dopa suggests a promising approach for controlling both dyskinesia and motor fluctuations in Parkinson's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Fahn S. How do you treat motor complications in Parkinson’s disease: Medicine, surgery, or both? Ann Neurol. 2008;64(Suppl 2):S56–S64. - PubMed
-
- Bezard E, Gross CE, Qin L, Gurevich VV, Benovic JL, Gurevich EV. L-DOPA reverses the MPTP-induced elevation of the arrestin2 and GRK6 expression and enhanced ERK activation in monkey brain. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;18:323–335. - PubMed
-
- Bychkov E, Ahmed MR, Dalby KN, Gurevich EV. Dopamine depletion and subsequent treatment with L-DOPA, but not the long-lived dopamine agonist pergolide, enhances activity of the Akt pathway in the rat striatum. J Neurochem. 2007;102:699–711. - PubMed
-
- Sgambato-Faure V, Buggia V, Gilbert F, Lévesque D, Benabid AL, Berger F. Coordinated and spatial upregulation of arc in striatonigral neurons correlates with L-dopa-induced behavioral sensitization in dyskinetic rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005;64:936–947. - PubMed
-
- Aubert I, Guigoni C, Håkansson K, Li Q, Dovero S, Barthe N, Bioulac BH, Gross CE, Fisone G, Bloch B, Bezard E. Increased D1 dopamine receptor signaling in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:17–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

