Chemical genetics strategy identifies an HCV NS5A inhibitor with a potent clinical effect
- PMID: 20410884
- PMCID: PMC7094952
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08960
Chemical genetics strategy identifies an HCV NS5A inhibitor with a potent clinical effect
Abstract
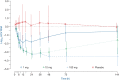
The worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is estimated to be approaching 200 million people. Current therapy relies upon a combination of pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin, a poorly tolerated regimen typically associated with less than 50% sustained virological response rate in those infected with genotype 1 virus. The development of direct-acting antiviral agents to treat HCV has focused predominantly on inhibitors of the viral enzymes NS3 protease and the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase NS5B. Here we describe the profile of BMS-790052, a small molecule inhibitor of the HCV NS5A protein that exhibits picomolar half-maximum effective concentrations (EC(50)) towards replicons expressing a broad range of HCV genotypes and the JFH-1 genotype 2a infectious virus in cell culture. In a phase I clinical trial in patients chronically infected with HCV, administration of a single 100-mg dose of BMS-790052 was associated with a 3.3 log(10) reduction in mean viral load measured 24 h post-dose that was sustained for an additional 120 h in two patients infected with genotype 1b virus. Genotypic analysis of samples taken at baseline, 24 and 144 h post-dose revealed that the major HCV variants observed had substitutions at amino-acid positions identified using the in vitro replicon system. These results provide the first clinical validation of an inhibitor of HCV NS5A, a protein with no known enzymatic function, as an approach to the suppression of virus replication that offers potential as part of a therapeutic regimen based on combinations of HCV inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are or were, at the time this work was conducted, employees of Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Figures



Comment in
-
Hepatitis C: An unsuspected drug target.Nature. 2010 May 6;465(7294):42-4. doi: 10.1038/465042a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20445618 No abstract available.
-
Antiviral drugs: New oral HCV drug shows promise.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Jun;9(6):432. doi: 10.1038/nrd3189. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 20514066 No abstract available.
-
Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A inhibitors: novel target-now for new trials and new treatment strategies.Hepatology. 2010 Sep;52(3):1162-4. doi: 10.1002/hep.23853. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20812360 No abstract available.
-
NS5A inhibitors: a new breakthrough for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C.J Hepatol. 2011 May;54(5):1069-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.033. Epub 2010 Dec 16. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21167889 No abstract available.
-
New oral HCV drug shows promise.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 Jul;8(7):464. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2396. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21394952 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

