Cyanobacterial cyclopeptides as lead compounds to novel targeted cancer drugs
- PMID: 20411119
- PMCID: PMC2857373
- DOI: 10.3390/md8030629
Cyanobacterial cyclopeptides as lead compounds to novel targeted cancer drugs
Abstract
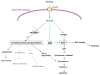
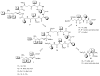
Cyanobacterial cyclopeptides, including microcystins and nodularins, are considered a health hazard to humans due to the possible toxic effects of high consumption. From a pharmacological standpoint, microcystins are stable hydrophilic cyclic heptapeptides with a potential to cause cellular damage following uptake via organic anion-transporting polypeptides (OATP). Their intracellular biological effects involve inhibition of catalytic subunits of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) and PP2, glutathione depletion and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Interestingly, certain OATPs are prominently expressed in cancers as compared to normal tissues, qualifying MC as potential candidates for cancer drug development. In the era of targeted cancer therapy, cyanotoxins comprise a rich source of natural cytotoxic compounds with a potential to target cancers expressing specific uptake transporters. Moreover, their structure offers opportunities for combinatorial engineering to enhance the therapeutic index and resolve organ-specific toxicity issues. In this article, we revisit cyanobacterial cyclopeptides as potential novel targets for anticancer drugs by summarizing existing biomedical evidence, presenting structure-activity data and discussing developmental perspectives.
Keywords: OATP; cancer; cyanobacteria; cyanotoxins; membrane transporters; microcystin; targeted-therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Awramik SM. The oldest records of photosynthesis. Photosynth Res. 1992;33:75–89. - PubMed
-
- Blank CE, Sanchez-Baracaldo P. Timing of morphological and ecological innovations in the cyanobacteria–a key to understanding the rise in atmospheric oxygen. Geobiology. 2010;8:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Zehr JP, Waterbury JB, Turner PJ, Montoya JP, Omoregie E, Steward GF, Hansen A, Karl DM. Unicellular cyanobacteria fix N2 in the subtropical North Pacific Ocean. Nature. 2001;412:635–638. - PubMed
-
- Francis G. Poisonous Australian lake. Nature. 1878;18:11–12.
-
- Gupta N, Pant SC, Vijayaraghavan R, Rao PV. Comparative toxicity evaluation of cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin variants (LR, RR, YR) in mice. Toxicology. 2003;188:285–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
