A functional ABCA1 gene variant is associated with low HDL-cholesterol levels and shows evidence of positive selection in Native Americans
- PMID: 20418488
- PMCID: PMC2893805
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq173
A functional ABCA1 gene variant is associated with low HDL-cholesterol levels and shows evidence of positive selection in Native Americans
Abstract
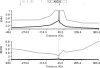
It has been suggested that the higher susceptibility of Hispanics to metabolic disease is related to their Native American heritage. A frequent cholesterol transporter ABCA1 (ATP-binding cassette transporter A1) gene variant (R230C, rs9282541) apparently exclusive to Native American individuals was associated with low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels, obesity and type 2 diabetes in Mexican Mestizos. We performed a more extensive analysis of this variant in 4405 Native Americans and 863 individuals from other ethnic groups to investigate genetic evidence of positive selection, to assess its functional effect in vitro and to explore associations with HDL-C levels and other metabolic traits. The C230 allele was found in 29 of 36 Native American groups, but not in European, Asian or African individuals. C230 was observed on a single haplotype, and C230-bearing chromosomes showed longer relative haplotype extension compared with other haplotypes in the Americas. Additionally, single-nucleotide polymorphism data from the Human Genome Diversity Panel Native American populations were enriched in significant integrated haplotype score values in the region upstream of the ABCA1 gene. Cells expressing the C230 allele showed a 27% cholesterol efflux reduction (P< 0.001), confirming this variant has a functional effect in vitro. Moreover, the C230 allele was associated with lower HDL-C levels (P = 1.77 x 10(-11)) and with higher body mass index (P = 0.0001) in the combined analysis of Native American populations. This is the first report of a common functional variant exclusive to Native American and descent populations, which is a major determinant of HDL-C levels and may have contributed to the adaptive evolution of Native American populations.
Figures



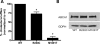
References
-
- Lorenzo C., Serrano-Rios M., Martinez-Larrad M.T., Gabriel R., Williams K., Gonzalez-Villalpando C., Stern M.P., Hazuda H.P., Haffner S.M. Was the historic contribution of Spain to the Mexican gene pool partially responsible for the higher prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Mexican-origin populations? The Spanish Insulin Resistance Study Group, the San Antonio Heart Study, and the Mexico City Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:2059–2064. doi:10.2337/diacare.24.12.2059. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cossrow N., Falkner B. Race/ethnic issues in obesity and obesity-related comorbidities. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004;89:2590–2594. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0339. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Salinas C.A., Canizales-Quinteros S., Rojas-Martínez R., Mehta R., Villarreal-Molina M.T., Arellano-Campos O., Riba L., Gómez-Pérez F.J., Tusié-Luna M.T. Hypoalphalipoproteinemia in the populations with Native American origin: an opportunity to assess the interaction of genes and environment. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2009;20:92–97. doi:10.1097/MOL.0b013e3283295e96. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Villarreal-Molina M.T., Aguilar-Salinas C.A., Rodriguez-Cruz M., Riaño D., Villalobos-Comparan M., Coral-Vazquez R., Menjivar M., Yescas-Gomez P., Königsoerg-Fainstein M., Romero-Hidalgo S., et al. The ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 R230C variant affects HDL cholesterol levels and BMI in the Mexican population: association with obesity and obesity-related comorbidities. Diabetes. 2007;56:1881–1887. doi:10.2337/db06-0905. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Villarreal-Molina M.T., Flores-Dorantes M.T., Arellano-Campos O., Villalobos-Comparan M., Rodríguez-Cruz M., Miliar-García A., Huertas-Vazquez A., Menjivar M., Romero-Hidalgo S., Wacher N.H., et al. Association of the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 R230C variant with early-onset type 2 diabetes in a Mexican population. Diabetes. 2008;57:509–513. doi:10.2337/db07-0484. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

