Chordin-induced lineage plasticity of adult SVZ neuroblasts after demyelination
- PMID: 20418875
- PMCID: PMC4059417
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2536
Chordin-induced lineage plasticity of adult SVZ neuroblasts after demyelination
Abstract
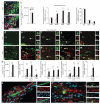
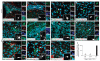
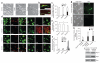
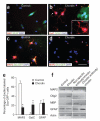
The mechanisms that regulate the developmental potential of adult neural progenitor populations under physiological and pathological conditions remain poorly defined. Glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 (GAD65)- and Doublecortin (Dcx)-expressing cells constitute major progenitor populations in the adult mouse subventricular zone (SVZ). Under normal physiological conditions, SVZ-derived GAD65-positive and Dcx-positive cells expressed the transcription factor Pax6 and migrated along the rostral migratory stream to the olfactory bulb to generate interneurons. After lysolecithin-induced demyelination of corpus callosum, however, these cells altered their molecular and cellular properties and migratory path. Demyelination upregulated chordin in the SVZ, which redirected GAD65-positive and Dcx-positive progenitors from neuronal to glial fates, generating new oligodendrocytes in the corpus callosum. Our findings suggest that the lineage plasticity of SVZ progenitor cells could be a potential therapeutic strategy for diseased or injured brain.
Figures




References
-
- Palmer TD, Willhoite AR, Gage FH. Vascular niche for adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000;425:479–494. - PubMed
-
- Temple S. The development of neural stem cells. Nature. 2001;414:112–117. - PubMed
-
- Shen Q, Zhong W, Jan YN, Temple S. Asymmetric Numb distribution is critical for asymmetric cell division of mouse cerebral cortical stem cells and neuroblasts. Development. 2002;129:4843–4853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01NS045702/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG024984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD040677/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045702/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048271/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS048271/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG024984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MH084018/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS056427/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS056427/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R33 MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EY017203/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES021957/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30HD40677/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K99 NS057944/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K99NS057944/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

