Pol II and its associated epigenetic marks are present at Pol III-transcribed noncoding RNA genes
- PMID: 20418881
- PMCID: PMC2917008
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1806
Pol II and its associated epigenetic marks are present at Pol III-transcribed noncoding RNA genes
Abstract
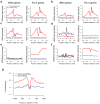
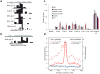
Epigenetic control is an important aspect of gene regulation. Despite detailed understanding of protein-coding gene expression, the transcription of noncoding RNA genes by RNA polymerase III (Pol III) is less well characterized. Here we profile the epigenetic features of Pol III target genes throughout the human genome. This reveals that the chromatin landscape of Pol III-transcribed genes resembles that of Pol II templates in many ways, although there are also clear differences. Our analysis also uncovered an entirely unexpected phenomenon: namely, that Pol II is present at the majority of genomic loci that are bound by Pol III.
Figures

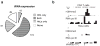

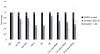
References
-
- Dieci G, et al. The expanding RNA polymerase III transcriptome. Trends Genet. 2007;23:614–622. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z, et al. The 7SK small nuclear RNA inhibits the CDK9/cyclin T1 kinase to control transcription. Nature. 2001;414:317–322. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen VT, et al. 7SK small nuclear RNA binds to and inhibits the activity of CDK9/cyclin T complexes. Nature. 2001;414:322–325. - PubMed
-
- Mossink MH, van Zon A, Scheper RJ, Sonneveld P, Wiemer EAC. Vaults: a ribonucleoprotein particle involved in drug resistance? Oncogene. 2003;22:7458–7467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

